Acute kidney injury in non-severe pneumonia is associated with an increased immune response and lower survival
- PMID: 20032961
- PMCID: PMC2871010
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2009.502
Acute kidney injury in non-severe pneumonia is associated with an increased immune response and lower survival
Abstract
While sepsis is a leading cause of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients, the relationship between immune response and acute kidney injury in less severely ill patients with infection is not known. Here we studied the epidemiology, 1-year mortality, and immune response associated with acute kidney injury in 1836 hospitalized patients with community-acquired severe and non-severe pneumonia. Acute kidney injury developed in 631 patients of whom 329 had severe and 302 had non-severe sepsis. Depending on the subgroup classification, 16-25% of the patients with non-severe pneumonia also developed acute kidney injury. In general, patients with acute kidney injury were older, had more comorbidity, and had higher biomarker concentrations (interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor, D-dimer) even among patients without severe sepsis. The risk of death associated with acute kidney injury varied when assessed by Gray's survival model and after adjusting for differences in age, gender, ethnicity, and comorbidity. This risk was significantly higher immediately after hospitalization but gradually fell over time in the overall cohort and in those with non-severe pneumonia. A significantly higher risk of death (hazard ratio 1.29) was also present in those never admitted to an intensive care unit. Hence acute kidney injury is common even among patients with non-severe pneumonia and is associated with higher immune response and an increased risk of death.
Figures

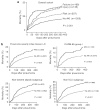
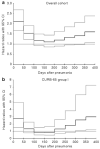
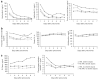
Comment in
-
Acute kidney injury in sepsis: questions answered, but others remain.Kidney Int. 2010 Mar;77(6):485-7. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.517. Kidney Int. 2010. PMID: 20186161
-
The value of plasma pro-enkephalin and adrenomedullin for the prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients.Crit Care. 2020 Apr 21;24(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02887-6. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32316998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, et al. Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: clinical characteristics and outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:431–439. - PubMed
-
- Schrier RW, Wang W. Acute renal failure and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Chen YC, Jenq CC, Tian YC, et al. RIFLE classification for predicting in-hospital mortality in critically ill sepsis patients. Shock. 2009;31:139–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

