Prototypic GABA(A) receptor agonist muscimol acts preferentially through forebrain high-affinity binding sites
- PMID: 20032968
- PMCID: PMC2823376
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.203
Prototypic GABA(A) receptor agonist muscimol acts preferentially through forebrain high-affinity binding sites
Abstract
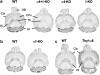
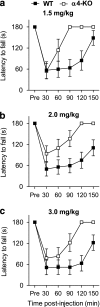
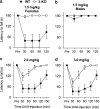
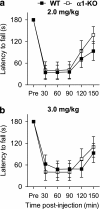
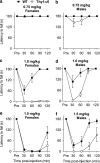
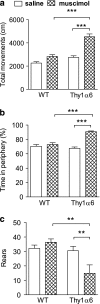
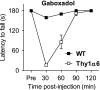
Muscimol has been regarded as a universal agonist for all gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABA(A)-R) subtypes. However, brain regional distribution of muscimol's high-affinity binding sites greatly differs from those of other binding sites of the GABA(A)-R. To test whether behavioral effects of muscimol correlated with the density of high-affinity [(3)H]muscimol binding, we examined several GABA(A)-R subunit gene-modified mouse lines: alpha1, alpha4, or delta-knockouts (KO), alpha4+delta-double KO, and Thy1.2 promoter-driven alpha6 transgenic mice (Thy1alpha6). We determined the high-affinity [(3)H]muscimol binding in brain sections by quantitative autoradiography and sedative/ataxic effects induced in vivo by muscimol using a constant speed rotarod. alpha4-KO mice had reduced [(3)H]muscimol binding in the caudate-putamen, thalamus, and hippocampus, and were less sensitive to the behavioral impairment by muscimol. Similarly, delta-KO mice also had reduced binding to forebrain regions and a lower behavioral sensitivity to muscimol than their wild-type controls. In contrast, alpha1-KO mice had unaltered behavioral sensitivity to muscimol and unaltered [(3)H]muscimol binding, even though previous studies have demonstrated dramatically reduced binding to various other GABA(A)-R sites in these mice. Finally, Thy1alpha6 mice exhibited increased behavioral sensitivity to muscimol, and to another direct GABA-site agonist gaboxadol, and increased [(3)H]muscimol binding in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Thus, the differences in sedative and motor-impairing actions of muscimol in various mouse models correlated with the level of forebrain high-affinity [(3)H]muscimol binding. These data suggest that a small special population of GABA(A)-Rs, most likely extrasynaptic non-alpha1-containing receptors, strongly contributes to the in vivo pharmacological effects of muscimol.
Figures
References
-
- Agey MW, Dunn SM. Kinetics of [3H]muscimol binding to the GABAA receptor in bovine brain membranes. Biochemistry. 1989;28:4200–4208. - PubMed
-
- Amin J, Weiss DS. GABAA receptor needs two homologous domains of the β-subunit for activation by GABA but not by pentobarbital. Nature. 1993;366:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Backus KH, Arigoni M, Drescher U, Scheurer L, Malherbe P, Mohler H, et al. Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor deduced from mutation-induced rectification. Neuroreport. 1993;5:285–288. - PubMed
-
- Baraldi M, Grandison L, Guidotti A. Distribution and metabolism of muscimol in the brain and other tissues of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1979;18:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:291–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

