Patient preference and acceptability of calcium plus vitamin D3 supplementation: a randomised, open, cross-over trial
- PMID: 20033244
- PMCID: PMC2843840
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-009-1328-3
Patient preference and acceptability of calcium plus vitamin D3 supplementation: a randomised, open, cross-over trial
Abstract
Preference for a drug formulation is important in adherence to long-term medication for chronic illnesses such as osteoporosis. We investigated the preference for and acceptability of chewable tablet containing calcium and vitamin D (Calci Chew D(3), Nycomed) compared to that of a sachet containing calcium and vitamin D(3) (Cad, Will-Pharma). This open, randomised, cross-over trial was set up to compare the preference and acceptability of two calcium plus vitamin D(3) formulations (both with 500 mg calcium and 400/440 IU vitamin D3), given twice a day in patients with osteoporosis. Preference and acceptability were assessed by means of questionnaires. Preference was determined by asking the question, which treatment the patient preferred, and acceptability was measured by scoring five variables, using rating scales. Of the 102 patients indicating a preference for a trial medication, 67% preferred the chewable tablet, 19% the sachet with calcium and vitamin D(3,) and 15% stated no preference. The significant preference for Calci Chew D(3) (p < 0.0001) was associated with higher scores for all five acceptability variables. The two formulations were tolerated equally well. A significant greater number of patients considered the chewable tablet as preferable and acceptable to the sachet, containing calcium and vitamin D(3).
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN18822358.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was sponsored by Nycomed Group AS/Roskilde, Denmark.
Figures
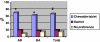
References
-
- Cooper C, Atkinson EJ, Jacobsen SJ, O'Fallon WM, Melton LJ., III Population-based study of survival after osteoporotic fractures. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;137:1001–1005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

