Intraoperative localization of insulinoma and normal pancreas using invisible near-infrared fluorescent light
- PMID: 20033320
- PMCID: PMC2841719
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-009-0868-8
Intraoperative localization of insulinoma and normal pancreas using invisible near-infrared fluorescent light
Abstract
Background: Neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas, such as insulinoma, are difficult to localize, and complete resection is essential for cure. Our hypothesis is that a near-infrared (NIR) fluorophore exhibiting uptake in insulinoma could provide high-sensitivity detection intraoperatively.
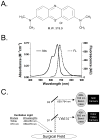
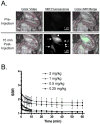
Materials and methods: The optical properties of methylene blue (MB) were measured in vitro in 100% serum at 37 degrees C and in vivo after tissue uptake. MB was injected as a rapid intravenous bolus at doses ranging from 0.25 to 2 mg/kg into wildtype rats and pigs, and into insulinoma-bearing transgenic mice. The FLARE imaging system was used to acquire color video and NIR fluorescence images simultaneously and in real-time. The signal-to-background ratios (SBR) of tissues and tumors were quantified using FLARE software.
Results: When appropriately diluted, MB exhibits moderate NIR fluorescence emission peaking at 688 nm. At doses > or =1 mg/kg, certain normal tissues, such as pancreas, accumulate MB and remain NIR fluorescent for up to 1 h with an SBR > or = 1.6. MB spectral properties are maintained after uptake into tissue. Interestingly, insulinoma exhibits even higher MB signal than normal pancreas, resulting in insulinoma-to-pancreas ratios of 3.7 and insulinoma-to-muscle ratios of 16.2. MB permitted high-sensitivity, real-time localization of primary, multicentric, and metastatic insulinoma and permitted differentiation among tumor, normal pancreas, and other abdominal structures.
Conclusion: A single intravenous injection of a clinically available, commonly used NIR fluorophore provides prolonged intraoperative localization of normal pancreas and insulinoma using invisible NIR fluorescent light.
Keywords: Intraoperative Imaging; Methylene Blue; Near-Infrared Fluorescence; Neuroendocrine Tumors; Pancreas.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pancreas-targeted NIR fluorophores for dual-channel image-guided abdominal surgery.Theranostics. 2015 Jan 1;5(1):1-11. doi: 10.7150/thno.10259. eCollection 2015. Theranostics. 2015. PMID: 25553094 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time assessment of cardiac perfusion, coronary angiography, and acute intravascular thrombi using dual-channel near-infrared fluorescence imaging.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009 Jul;138(1):133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.09.082. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009. PMID: 19577070 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time intraoperative assessment of the extrahepatic bile ducts in rats and pigs using invisible near-infrared fluorescent light.Surgery. 2008 Jul;144(1):39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2008.03.017. Epub 2008 May 27. Surgery. 2008. PMID: 18571583 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Localization and Resection of Small Pancreatic Cystic Insulinoma Using Intraoperative Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging: A Case Report and Literature Review.Pancreas. 2020 Nov/Dec;49(10):1388-1392. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001678. Pancreas. 2020. PMID: 33122530 Review.
-
Mangan-enhanced MR imaging for the detection and localisation of small pancreatic insulinoma.Eur Radiol. 2004 May;14(5):923-5. doi: 10.1007/s00330-003-2017-2. Epub 2003 Sep 3. Eur Radiol. 2004. PMID: 12955450 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-specific fluorescence antibody imaging enables accurate staging laparoscopy in an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer.Hepatogastroenterology. 2012 Sep;59(118):1994-9. doi: 10.5754/hge11836. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22369743 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence-Guided Surgery.Front Oncol. 2017 Dec 22;7:314. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00314. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29312886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of a solitary fibrous tumor of the pancreas using methylene blue.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2012 Jul 27;4(7):180-4. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v4.i7.180. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2012. PMID: 22905287 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and future perspectives of fluorescence-guided surgery for cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016;16(1):71-81. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2016.1121109. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26567611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-targeted Nucleic Acid Delivery and Quantum Dot Imaging Using EGF Receptor Aptamer-conjugated Lipid Nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 25;7(1):9474. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09555-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28842588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tucker ON, Crotty PL, Conlon KC. The management of insulinoma. Br J Surg. 2006;93:264–75. - PubMed
-
- Warner RR. Enteroendocrine tumors other than carcinoid: a review of clinically significant advances. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1668–84. - PubMed
-
- Pedrazzoli S, Pasquali C, Alfano D’Andrea A. Surgical treatment of insulinoma. Br J Surg. 1994;81:672–6. - PubMed
-
- McAuley G, Delaney H, Colville J, Lyburn I, Worsley D, Govender P, Torreggiani WC. Multimodality preoperative imaging of pancreatic insulinomas. Clin Radiol. 2005;60:1039–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

