Nitrosamine exposure exacerbates high fat diet-mediated type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and neurodegeneration with cognitive impairment
- PMID: 20034403
- PMCID: PMC2803782
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-54
Nitrosamine exposure exacerbates high fat diet-mediated type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and neurodegeneration with cognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: The current epidemics of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and Alzheimer's disease (AD) all represent insulin-resistance diseases. Previous studies linked insulin resistance diseases to high fat diets or exposure to streptozotocin, a nitrosamine-related compound that causes T2DM, NASH, and AD-type neurodegeneration. We hypothesize that low-level exposure to nitrosamines that are widely present in processed foods, amplifies the deleterious effects of high fat intake in promoting T2DM, NASH, and neurodegeneration.
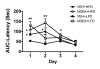
Methods: Long Evans rat pups were treated with N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) by i.p. Injection, and upon weaning, they were fed with high fat (60%; HFD) or low fat (5%; LFD) chow for 6 weeks. Rats were evaluated for cognitive impairment, insulin resistance, and neurodegeneration using behavioral, biochemical, molecular, and histological methods.
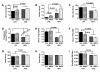
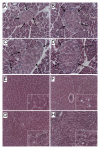
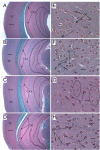
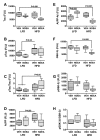
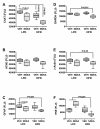
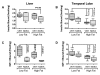
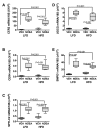
Results: NDEA and HFD +/- NDEA caused T2DM, NASH, deficits in spatial learning, and neurodegeneration with hepatic and brain insulin and/or IGF resistance, and reductions in tau and choline acetyltransferase levels in the temporal lobe. In addition, pro-ceramide genes, which promote insulin resistance, were increased in livers and brains of rats exposed to NDEA, HFD, or both. In nearly all assays, the adverse effects of HFD+NDEA were worse than either treatment alone.
Conclusions: Environmental and food contaminant exposures to low, sub-mutagenic levels of nitrosamines, together with chronic HFD feeding, function synergistically to promote major insulin resistance diseases including T2DM, NASH, and AD-type neurodegeneration. Steps to minimize human exposure to nitrosamines and consumption of high-fat content foods are needed to quell these costly and devastating epidemics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early limited nitrosamine exposures exacerbate high fat diet-mediated type 2 diabetes and neurodegeneration.BMC Endocr Disord. 2010 Mar 19;10:4. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-10-4. BMC Endocr Disord. 2010. PMID: 20302640 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrosamine exposure causes insulin resistance diseases: relevance to type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;17(4):827-44. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. PMID: 20387270 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic ceramide may mediate brain insulin resistance and neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;16(4):715-29. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2009-0984. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. PMID: 19387108 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemilogical trends strongly suggest exposures as etiologic agents in the pathogenesis of sporadic Alzheimer's disease, diabetes mellitus, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;17(3):519-29. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2009-1070. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. PMID: 19363256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain metabolic dysfunction at the core of Alzheimer's disease.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 15;88(4):548-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24380887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Replacements for Saturated Fat to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk.Healthcare (Basel). 2017 Jun 21;5(2):29. doi: 10.3390/healthcare5020029. Healthcare (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28635680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain insulin resistance and deficiency as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012 Jan;9(1):35-66. doi: 10.2174/156720512799015037. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012. PMID: 22329651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agent Orange Herbicidal Toxin-Initiation of Alzheimer-Type Neurodegeneration.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(4):1703-1726. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230881. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38306038 Free PMC article.
-
End-stage renal disease and metalworking fluid exposure.Occup Environ Med. 2022 Jan;79(1):24-31. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2020-106715. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Occup Environ Med. 2022. PMID: 34210793 Free PMC article.
-
Gallium Nanoparticle-Mediated Reduction of Brain Specific Serine Protease-4 in an Experimental Metastatic Cancer Model.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Apr 1;18(4):895-903. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.4.895. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 28545186 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

