Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors reduce atherosclerosis in a double-injury rabbit model
- PMID: 20034432
- PMCID: PMC2798842
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors reduce atherosclerosis in a double-injury rabbit model
Abstract
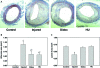
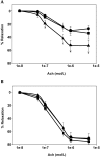
Atheroproliferative disorders such as atherosclerosis are an important health problem and one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the United States. Minimally invasive therapeutic procedures, including angioplasty with stent deployment, are used frequently for obstructive coronary artery disease. However, restenosis, a proliferative vascular response, is a common sequela to this procedure. The current study investigated the effect of inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase (RR), an enzyme necessary for cellular proliferation, in an attempt to ameliorate the proliferative response. Two RR inhibitors, didox and hydroxyurea, were chosen for their potent antiproliferative properties. Studies were carried out by using a double-injury rabbit model, in which endothelial denudation was followed by the administration of a high-fat diet. At 4 wk after initial endothelial denudation, the developing atherosclerotic lesion was subjected to transluminal balloon dilation to simulate clinical intervention with percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. The degree of restenosis and atheroproliferation was assessed at 8 wk. Histologic evaluation of the lesion demonstrated that treatment with didox and hydroxyurea significantly decreased lesion area and lumen loss. These results suggest that RR inhibition may be an effective new tool for the treatment of atheroproliferative disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Beyar R. 2004. Novel approaches to reduce restenosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1015:367–378 - PubMed
-
- Drachman DE, Edelman ER, Seifert P, Groothuis AR, Bornstein DA, Kamath KR, Palasis M, Yang D, Nott SH, Rogers C. 2000. Neointimal thickening after stent delivery of paclitaxel: change in composition and arrest of growth over 6 months. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2325–2332 - PubMed
-
- Duilio C, Ambrosio G, Kuppusamy P, DiPaula A, Becker LC, Zweier JL. 2001. Neutrophils are primary source of O2 radicals during reperfusion after prolonged myocardial ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H2649–H2657 - PubMed
-
- Elezi S, Kastrati A, Neumann FJ, Hadamitzky M, Dirschinger J, Schomig A. 1998. Vessel size and long-term outcome after coronary stent placement. Circulation 98:1875–1880 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
