Epidemiology of invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae with hypermucoviscosity phenotype in a research colony of nonhuman primates
- PMID: 20034435
- PMCID: PMC2798845
Epidemiology of invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae with hypermucoviscosity phenotype in a research colony of nonhuman primates
Abstract
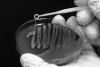
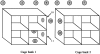
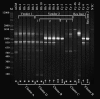
Invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae with hypermucoviscosity phenotype (HMV K. pneumoniae) is an emerging human pathogen that, over the past 20 y, has resulted in a distinct clinical syndrome characterized by pyogenic liver abscesses sometimes complicated by bacteremia, meningitis, and endophthalmitis. Infections occur predominantly in Taiwan and other Asian countries, but HMV K. pneumoniae is considered an emerging infectious disease in the United States and other Western countries. In 2005, fatal multisystemic disease was attributed to HMV K. pneumoniae in African green monkeys (AGM) at our institution. After identification of a cluster of subclinically infected macaques in March and April 2008, screening of all colony nonhuman primates by oropharyngeal and rectal culture revealed 19 subclinically infected rhesus and cynomolgus macaques. PCR testing for 2 genes associated with HMV K. pneumoniae, rmpA and magA, suggested genetic variability in the samples. Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis on a subset of clinical isolates confirmed a high degree of genetic diversity between the samples. Environmental testing did not reveal evidence of aerosol or droplet transmission of the organism in housing areas. Further research is needed to characterize HMV K. pneumoniae, particularly with regard to genetic differences among bacterial strains and their relationship to human disease and to the apparent susceptibility of AGM to this organism.
Figures

References
-
- Chan KS, Yu WL, Tsai CL, Cheng KC, Hou CC, Lee MC, Tan CK. 2007. Pyogenic liver abscess caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: analysis of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of 84 patients. Chin Med J (Engl) 120:136–139 - PubMed
-
- Chang CM, Lu FH, Guo HR, Ko WC. 2005. Klebsiella pneumoniae fascial space infections of the head and neck in Taiwan: emphasis on diabetic patients and repetitive infections. J Infect 50:34–40 - PubMed
-
- Chuang YP, Fang CT, Lai SY, Chang SC, Wang JT. 2006. Genetic determinants of capsular serotype K1 of Klebsiella pneumoniae causing primary pyogenic liver abscess. J Infect Dis 193:645–654 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
