Orexin mediates morphine place preference, but not morphine-induced hyperactivity or sensitization
- PMID: 20034477
- PMCID: PMC2822072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.035
Orexin mediates morphine place preference, but not morphine-induced hyperactivity or sensitization
Abstract
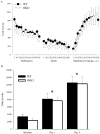
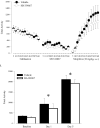
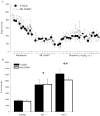
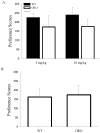
Orexin (or hypocretin) has been implicated in mediating drug addiction and reward. Here, we investigated orexin's contribution to morphine-induced behavioral sensitization and place preference. Orexin-/- (OKO) mice and littermate wild-type (WT) controls (n=56) and C57BL/6J mice (n=67) were tested for chronic morphine-induced locomotor sensitization or for conditioned place preference (CPP) for a morphine- or a cocaine-paired environment. C57BL/6J mice received the orexin receptor 1 (Ox1r) antagonist, SB-334867, prior to test sessions. OKO mice did not significantly differ from WT controls in locomotor activity following acute- or chronic-morphine treatments. Similarly, mice treated with the Ox1r antagonist did not differ from vehicle controls in locomotor activity following acute- or chronic-morphine treatments. In contrast, while OKO mice did not differ from WT controls in preference for a morphine-paired environment, the Ox1r antagonist significantly attenuated place preference for a morphine-, but not a cocaine-paired, environment. These data suggest that orexin action is not required for locomotor responses to acute and chronic morphine, but Ox1r signaling can influence morphine-seeking in WT animals.
2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of the orexin/hypocretin system in ethanol conditioned place preference.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Apr;214(4):805-18. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2082-6. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21107540 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin signaling via the orexin 1 receptor mediates operant responding for food reinforcement.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Apr 15;67(8):753-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.12.035. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20189166 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin/hypocretin signaling at the orexin 1 receptor regulates cue-elicited cocaine-seeking.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Aug;30(3):493-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06844.x. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19656173 Free PMC article.
-
Role of orexin/hypocretin in reward-seeking and addiction: implications for obesity.Physiol Behav. 2010 Jul 14;100(5):419-28. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.03.009. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Physiol Behav. 2010. PMID: 20338186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lateral hypothalamic orexin/hypocretin neurons: A role in reward-seeking and addiction.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:74-90. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.106. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19815001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orexin-1 Receptor Signaling in Ventral Pallidum Regulates Motivation for the Opioid Remifentanil.J Neurosci. 2019 Dec 4;39(49):9831-9840. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0255-19.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31641055 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin antagonists for neuropsychiatric disease: progress and potential pitfalls.Front Neurosci. 2014 Feb 25;8:36. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00036. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24616658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurobiological basis of narcolepsy.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Feb;20(2):83-93. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0097-x. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30546103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Seeking and Relapse: New Evidence of a Role for Orexin and Dynorphin Co-transmission in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Thalamus.Front Neurol. 2018 Aug 28;9:720. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00720. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30210441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staging perspectives in neurodevelopmental aspects of neuropsychiatry: agents, phases and ages at expression.Neurotox Res. 2010 Nov;18(3-4):287-305. doi: 10.1007/s12640-010-9162-6. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Neurotox Res. 2010. PMID: 20237881 Review.
References
-
- Borgland SL, Taha SA, Sarti F, Fields HL, Bonci A. Orexin A in the VTA is critical for the induction of synaptic plasticity and behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Neuron. 2006;49:589–601. - PubMed
-
- Borgland SL, Storm E, Bonci A. Orexin B/hypocretin 2 increases glutamatergic transmission to ventral tegmental area neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28:1545–56. - PubMed
-
- Boschen KE, Fadel JR, Burk JA. Systemic and intrabasalis administration of the orexin-1 receptor antagonist, SB-334867, disrupts attentional performance in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2009;206:205–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

