Regulatory function of cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+CD27-CD28- T cells
- PMID: 20034645
- PMCID: PMC2823847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.11.038
Regulatory function of cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+CD27-CD28- T cells
Abstract
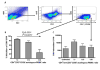
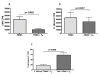
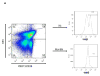
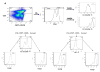
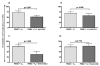
CMV infection is characterized by high of frequencies of CD27-CD28- T cells. Here we demonstrate that CMV-specific CD4+CD27-CD28- cells are regulatory T cells (TR). CD4+CD27-CD28- cells sorted from CMV-stimulated PBMC of CMV-seropositive donors inhibited de novo CMV-specific proliferation of autologous PBMC in a dose-dependent fashion. Compared with the entire CMV-stimulated CD4+ T-cell population, higher proportions of CD4+CD27-CD28- TR expressed FoxP3, TGFbeta, granzyme B, perforin, GITR and PD-1, lower proportions expressed CD127 and PD1-L and similar proportions expressed CD25, CTLA4, Fas-L and GITR-L. CMV-CD4+CD27-CD28- TR expanded in response to IL-2, but not to CMV antigenic restimulation. The anti-proliferative effect of CMV-CD4+CD27-CD28- TR significantly decreased after granzyme B or TGFbeta inhibition. The CMV-CD4+CD27-CD28- TR of HIV-infected and uninfected donors had similar phenotypes and anti-proliferative potency, but HIV-infected individuals had higher proportions of CMV-CD4+CD27-CD28- TR. The CMV-CD4+CD27-CD28- TR may contribute to the downregulation of CMV-specific and nonspecific immune responses of CMV-infected individuals.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
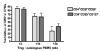



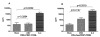
References
-
- Adeegbe D, Bayer AL, Levy RB, Malek TR. Cutting edge: allogeneic CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells suppress autoimmunity while establishing transplantation tolerance. J Immunol. 2006;176 (12):7149–53. - PubMed
-
- Almanzar G, Schwaiger S, Jenewein B, Keller M, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Wurzner R, Schonitzer D, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. Long-term cytomegalovirus infection leads to significant changes in the composition of the CD8+ T-cell repertoire, which may be the basis for an imbalance in the cytokine production profile in elderly persons. J Virol. 2005;79 (6):3675–83. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bekker V, Bronke C, Scherpbier HJ, Weel JF, Jurriaans S, Wertheim-van Dillen PM, van Leth F, Lange JM, Tesselaar K, van Baarle D, Kuijpers TW. Cytomegalovirus rather than HIV triggers the outgrowth of effector CD8+CD45RA+CD27− T cells in HIV-1-infected children. Aids. 2005;19 (10):1025–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

