Long-term efficacy results of EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 3 study 30911 comparing intravesical instillations of epirubicin, bacillus Calmette-Guérin, and bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus isoniazid in patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
- PMID: 20034729
- PMCID: PMC2889174
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.12.024
Long-term efficacy results of EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 3 study 30911 comparing intravesical instillations of epirubicin, bacillus Calmette-Guérin, and bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus isoniazid in patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
Abstract
Background: Intravesical chemotherapy and bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) reduce the recurrence rate in patients with stage Ta T1 urothelial bladder cancer; however, the benefit of BCG relative to chemotherapy for long-term end points is controversial, especially in intermediate-risk patients.
Objective: The aim of the study was to compare the long-term efficacy of BCG and epirubicin.
Design, setting, and participants: From January 1992 to February 1997, 957 patients with intermediate- or high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial bladder cancer were randomized after transurethral resection to one of three treatment groups in the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Genito-Urinary Group phase 3 trial 30911.
Intervention: Patients received six weekly instillations of epirubicin, BCG, or BCG plus isoniazid (INH) followed by three weekly maintenance instillations at months 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36.
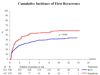
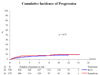
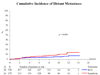
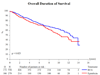
Measurements: End points were time to recurrence, progression, distant metastases, overall survival, and disease-specific survival.
Results and limitations: With 837 eligible patients and a median follow-up of 9.2 yr, time to first recurrence (p<0.001), distant metastases (p=0.046), overall survival (p=0.023), and disease-specific survival (p=0.026) were significantly longer in the two BCG arms combined as compared with epirubicin; however, there was no difference for progression. Three hundred twenty-three patients with stage T1 or grade 3 tumors were high risk, and the remaining 497 patients were intermediate risk. The observed treatment benefit was at least as large, if not larger, in the intermediate-risk patients compared with the high-risk patients.
Conclusions: In patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta and T1 urothelial bladder cancer, intravesical BCG with or without INH is superior to intravesical epirubicin not only for time to first recurrence but also for time to distant metastases, overall survival, and disease-specific survival. The benefit of BCG is not limited to just high-risk patients; intermediate-risk patients also benefit from BCG.
Trial registration: This study was registered with the US National Cancer Institute clinical trials database [protocol ID: EORTC-30911]. http://www.cancer.gov/search/ViewClinicalTrials.aspx?cdrid=77075&version=HealthProfessional&protocolsearchid=6540260.
Copyright © 2009 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
New insights in intravesical treatment for intermediate- and high-risk non-muscle-invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2010 May;57(5):774-6; author reply 776-7. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Eur Urol. 2010. PMID: 20080332 No abstract available.
-
Re: Richard J. Sylvester, Maurizio A. Brausi, Wim J. Kirkels, et al. Long-term efficacy results of EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 3 study 30911 comparing intravesical instillations of epirubicin, bacillus Calmette-Guérin, and bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus isoniazid in patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 2010;57:766-73.Eur Urol. 2010 Jun;57(6):e57; author reply e58-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.02.037. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Eur Urol. 2010. PMID: 20227819 No abstract available.
-
Words of wisdom. Re: Long-term efficacy results of EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 3 study 30911 comparing intravesical instillations of epirubicin, bacillus Calmette-Guérin, and bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus isoniazid in patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Sylvester RJ, Brausi MA, Kirkels WJ, et al.Eur Urol. 2011 Jun;59(6):1065. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.03.040. Eur Urol. 2011. PMID: 21531192 No abstract available.
References
-
- Babjuk M, Oosterlinck W, Sylvester R, Kasinen E, Bohle A, Palou-Redorta J. EAU guidelines on non–muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol. 2008;54:303–314. - PubMed
-
- Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006;49:466–477. - PubMed
-
- Shelley MD, Kynaston H, Court J, et al. A systematic review of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus transurethral resection vs transurethral resection alone in Ta and T1 bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2001;88:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Bohle A, Jocham D, Bock PR. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin versus mitomycin C for superficial bladder cancer: a formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on recurrence and toxicity. J Urol. 2003;169:90–95. - PubMed
-
- Malmstrom PU, Sylvester RJ, Crawford DE, et al. An individual patient data meta-analysis of the long-term outcome of randomized studies comparing intravesical mitomycin C versus bacillus Calmette-Guérin for non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2009;56:247–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

