Definitive hematopoiesis requires Runx1 C-terminal-mediated subnuclear targeting and transactivation
- PMID: 20035012
- PMCID: PMC2830828
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddp568
Definitive hematopoiesis requires Runx1 C-terminal-mediated subnuclear targeting and transactivation
Abstract
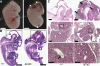
Runx1 is a key hematopoietic transcription factor required for definitive hematopoiesis and is a frequent target of leukemia-related chromosomal translocations. The resulting fusion proteins, while retaining DNA binding activity, display loss of subnuclear targeting and associated transactivation functions encoded by the C-terminus of the protein. To define the precise contribution of the Runx1 C-terminus in development and leukemia, we created a knock-in mouse with a C-terminal truncation by introducing a single nucleic acid substitution in the native Runx1 locus. This mutation (Runx1(Q307X)) models genetic lesions observed in patients with leukemia and myeloproliferative disorders. The Runx1(Q307X) homozygous mouse exhibits embryonic lethality at E12.5 due to central nervous system hemorrhages and a complete lack of hematopoietic stem cell function. While able to bind DNA, Runx1(Q307X) is unable to activate target genes, resulting in deregulation of various hematopoietic markers. Thus, we demonstrate that the subnuclear targeting and transcriptional regulatory activities of the Runx1 C-terminus are critical for hematopoietic development. We propose that compromising the C-terminal functions of Runx1 is a common mechanism for the pathological consequences of a variety of somatic mutations and Runx1-related leukemic fusion proteins observed in human patients.
Figures


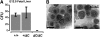

References
-
- Okuda T., van Deursen J., Hiebert S.W., Grosveld G., Downing J.R. AML1, the target of multiple chromosomal translocations in human leukemia, is essential for normal fetal liver hematopoiesis. Cell. 1996;84:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Motoda L., Osato M., Yamashita N., Jacob B., Chen L.Q., Yanagida M., Ida H., Wee H.J., Sun A.X., Taniuchi I., et al. Runx1 protects hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells from oncogenic insult. Stem Cells. 2007;25:2976–2986. - PubMed
-
- Kuo M.C., Liang D.C., Huang C.F., Shih Y.S., Wu J.H., Lin T.L., Shih L.Y. RUNX1 mutations are frequent in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and mutations at the C-terminal region might predict acute myeloid leukemia transformation. Leukemia. 2009;23:1426–1431. - PubMed
-
- Look A.T. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science. 1997;278:1059–1064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

