Genetic and proteomic features associated with survival after treatment with erlotinib in first-line therapy of non-small cell lung cancer in Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 3503
- PMID: 20035238
- PMCID: PMC3087978
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181c8cbd9
Genetic and proteomic features associated with survival after treatment with erlotinib in first-line therapy of non-small cell lung cancer in Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 3503
Abstract
Introduction: Serum proteomics and mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and KRAS have been associated with benefit after therapy with EGFR-targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer, but all three have not been evaluated in any one study.
Hypothesis: Pretreatment serum proteomics predicts survival in Western advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with wild-type EGFR and independent of KRAS mutation status.
Methods: We analyzed available biospecimens from Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 3503, a single-arm phase II study of erlotinib in first-line advanced lung cancer, for proteomics signatures in the previously described serum matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization proteomic classifier (VeriStrat) as well as for KRAS and EGFR mutations.
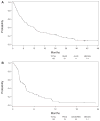
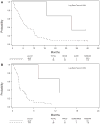
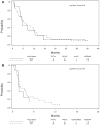
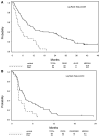
Results: Out of 137 enrolled patients, analyzable biologic samples were available on 102. Nine of 41 (22%) demonstrated KRAS mutations and 3 of 41 (7%) harbored EGFR mutations. VeriStrat classification identified 64 of 88 (73%) as predicted to have "good" and 24 of 88 (27%) predicted to have "poor" outcomes. A statistically significant correlation of VeriStrat status (p < 0.001) was found with survival. EGFR mutations, but not KRAS mutations, also correlated with survival.
Conclusions: The previously defined matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization predictor remains a potent and highly clinically significant predictor of survival after first-line treatment with erlotinib in patients with wild-type EGFR and independent of mutations in KRAS.
Figures
References
-
- Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) (corrected) J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2237–2246. - PubMed
-
- Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, et al. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer) Lancet. 2005;366:1527–1537. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Fong T, Morgensztern D, Govindan R. EGFR inhibitors as first-line therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:303–310. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R, et al. TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5892–5899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

