Microbead arrays for the analysis of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase activation and dimerization in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20035613
- PMCID: PMC3196214
- DOI: 10.1089/adt.2009.0208
Microbead arrays for the analysis of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase activation and dimerization in breast cancer cells
Abstract
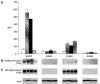
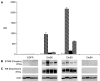
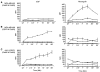
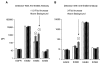
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in the ErbB family (EGFR, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4) are implicated in a variety of human malignancies. Accordingly, determination of both expression and activation (dimerization/heterodimerization and phosphorylation) of ErbB proteins is critical in defining their functional role in cancer. Efficient and comprehensive methods to study molecular functions of ErbB family of RTKs are needed not only for improvements in diagnostics but also for early screening of targeted drugs (eg, small molecule inhibitors and therapeutic antibodies). We report development of 3 multiplex microbead immunoassays for simultaneous detection of expression, protein-protein interactions, and phosphorylation of these RTKs. These novel multiplex immunoassays were used to study ErbB RTKs under different cell activation conditions in 2 breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-453 and MDA-MB-468) and an epidermoid cancer cell line (A431). The results were confirmed by immunoprecipitation/western blot. Importantly, the multiplex immunoassay facilitated time-course studies in these cell lines after cell activation with EGF and neuregulin, revealing the kinetics of phosphorylation of the ErbB family RTKs. This study demonstrates the utility of the Luminex(R) multiplex system as an efficient and comprehensive approach to study different aspects of molecular roles of these RTKs. Importantly, the study provides proof-of-concept for the utility of the multiplex microbead immunoassay approach for potential use in efficient, robust, and rapid screening of drugs, particularly those targeting functional aspects of these potent signaling molecules. In addition, the assays described here may be useful for cancer diagnostics and monitoring efficacy of therapy targeting the ErbB family of RTKs.
Figures
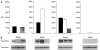

References
-
- Lo HW. Hsu SC. Hung MC. EGFR signaling pathway in breast cancers: from traditional signal transduction to direct nuclear translocalization. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;95:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Ono M. Kuwano M. Molecular mechanisms of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation and response to gefitinib and other EGFR-targeting drugs. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7242–7251. - PubMed
-
- Sweeney C. Miller JK. Shattuck DL. Carraway KL. ErbB receptor negative regulatory mechanisms: implications in cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006;11:89–99. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A. Gutteridge E. Gee JM. Nicholson RI. Robertson JF. Overview of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clinical breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(Suppl 1):S135–S144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

