PRNP variation in UK sporadic and variant Creutzfeldt Jakob disease highlights genetic risk factors and a novel non-synonymous polymorphism
- PMID: 20035629
- PMCID: PMC2806268
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-146
PRNP variation in UK sporadic and variant Creutzfeldt Jakob disease highlights genetic risk factors and a novel non-synonymous polymorphism
Abstract
Background: Genetic analysis of the human prion protein gene (PRNP) in suspect cases of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is necessary for accurate diagnosis and case classification. Previous publications on the genetic variation at the PRNP locus have highlighted the presence of numerous polymorphisms, in addition to the well recognised one at codon 129, with significant variability between geographically distinct populations. It is therefore of interest to consider their influence on susceptibility or the clinico-pathological disease phenotype. This study aimed to characterise the frequency and effect of PRNP open reading frame polymorphisms other than codon 129 in both disease and control samples sourced from the United Kingdom population.
Methods: DNA was extracted from blood samples and genetic data obtained by full sequence analysis of the prion protein gene or by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis using restriction enzymes specific to the gene polymorphism under investigation.
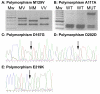
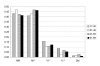
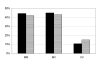
Results: 147 of 166 confirmed cases of variant CJD (vCJD) in the UK have had PRNP codon 129 genotyping and all are methionine homozygous at codon 129; 118 have had full PRNP gene sequencing. Of the latter, 5 cases have shown other polymorphic loci: at codon 219 (2, 1.69%), at codon 202 (2, 1.69%), and a 24 bp deletion in the octapeptide repeat region (1, 0.85%). E219K and D202D were not found in sporadic CJD (sCJD) cases and therefore may represent genetic risk factors for vCJD.Genetic analysis of 309 confirmed UK sCJD patients showed codon 129 genotype frequencies of MM: 59.5% (n = 184), MV: 21.4% (n = 66), and VV: 19.1% (n = 59). Thirteen (4.2%) had the A117A polymorphism, one of which also had the P68P polymorphism, four (1.3%) had a 24 bp deletion, and a single patient had a novel missense variation at codon 167. As the phenotype of this latter case is similar to sCJD and in the absence of a family history of CJD, it is unknown whether this is a form of genetic CJD, or simply a neutral polymorphism.
Conclusions: This analysis of PRNP genetic variation in UK CJD patients is the first to show a comprehensive comparison with healthy individuals (n = 970) from the same population, who were genotyped for the three most common variations (codon 129, codon 117, and 24 bp deletion). These latter two genetic variations were equally frequent in UK sCJD or vCJD cases and a normal (healthy blood donor) UK population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sporadic--but not variant--Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is associated with polymorphisms upstream of PRNP exon 1.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Dec;69(6):1225-35. doi: 10.1086/324710. Epub 2001 Nov 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11704923 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic risk factors for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a genome-wide association study.Lancet Neurol. 2009 Jan;8(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70265-5. Lancet Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19081515 Free PMC article.
-
A polymorphism in the regulatory region of PRNP is associated with increased risk of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.BMC Med Genet. 2011 May 22;12:73. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-73. BMC Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21600043 Free PMC article.
-
Variant CJD. 18 years of research and surveillance.Prion. 2014;8(4):286-95. doi: 10.4161/pri.29237. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Prion. 2014. PMID: 25495404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of PRNP polymorphisms on human prion disease susceptibility: an update.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Aug;130(2):159-70. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1447-7. Epub 2015 May 29. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 26022925 Review.
Cited by
-
Probing early misfolding events in prion protein mutants by NMR spectroscopy.Molecules. 2013 Aug 7;18(8):9451-76. doi: 10.3390/molecules18089451. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 23966072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the zoonotic potential of animal prion diseases: in vivo and in vitro approaches.Prion. 2014 Jan-Feb;8(1):85-91. doi: 10.4161/pri.28124. Prion. 2014. PMID: 24549113 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol for enhanced CJD surveillance in the 65+ years population group in Scotland: an observational neuropathological screening study of banked brain tissue donations for evidence of prion disease.BMJ Open. 2019 Oct 28;9(10):e033744. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033744. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31662408 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease surveillance in the older population: Assessment of a protocol for screening brain tissue donations for prion disease.Brain Pathol. 2024 Mar;34(2):e13214. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13214. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Brain Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37771100 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying prion disease penetrance using large population control cohorts.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Jan 20;8(322):322ra9. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad5169. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 26791950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wroe SJ, Pal S, Siddique D, Hyare H, Macfarlane R, Joiner S, Linehan JM, Brandner S, Wadsworth JD, Hewitt P, Collinge J. Clinical presentation and pre-mortem diagnosis of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with blood transfusion: a case report. Lancet. 2006;368:2061–2067. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69835-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

