Signal strength and signal duration define two distinct aspects of JNK-regulated axon stability
- PMID: 20035736
- PMCID: PMC2845820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.016
Signal strength and signal duration define two distinct aspects of JNK-regulated axon stability
Abstract
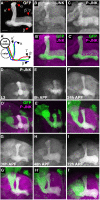
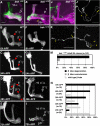
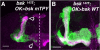
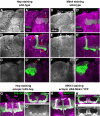
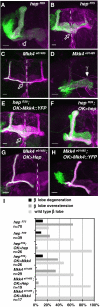
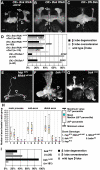
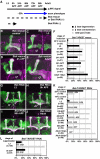
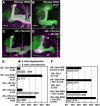
Signaling proteins often control multiple aspects of cell morphogenesis. Yet the mechanisms that govern their pleiotropic behavior are often unclear. Here we show activity levels and timing mechanisms determine distinct aspects of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway dependent axonal morphogenesis in Drosophila mushroom body (MB) neurons. In the complete absence of Drosophila JNK (Basket), MB axons fail to stabilize, leading to their subsequent degeneration. However, with a partial loss of Basket (Bsk), or of one of the upstream JNK kinases, Hemipterous or Mkk4, these axons overextend. This suggests that Bsk activity prevents axons from destabilizing, resulting in degeneration and overextension beyond their terminal targets. These distinct phenotypes require different threshold activities involving the convergent action of two distinct JNK kinases. We show that sustained Bsk signals are essential throughout development and act additively but are dispensable at adulthood. We also suggest that graded Bsk inputs are translated into AP-1 transcriptional outputs consisting of Fos and Jun proteins.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Agnes F., Suzanne M., Noselli S. The Drosophila JNK pathway controls the morphogenesis of imaginal discs during metamorphosis. Development. 1999;126:5453–5462. - PubMed
-
- Bettencourt-Dias M., Giet R., Sinka R., Mazumdar A., Lock W.G., Balloux F., Zafiropoulos P.J., Yamaguchi S., Winter S., Carthew R.W., Cooper M., Jones D., Frenz L., Glover D.M. Genome-wide survey of protein kinases required for cell cycle progression. Nature. 2004;432:980–987. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkblom B., Ostman N., Hongisto V., Komarovski V., Filen J.J., Nyman T.A., Kallunki T., Courtney M.J., Coffey E.T. Constitutively active cytoplasmic c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 is a dominant regulator of dendritic architecture: role of microtubule-associated protein 2 as an effector. J. Neurosci. 2005;25:6350–6361. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund M., Taipale M., Varjosalo M., Saharinen J., Lahdenpera J., Taipale J. Identification of pathways regulating cell size and cell-cycle progression by RNAi. Nature. 2006;439:1009–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

