Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) show robust primacy and recency in memory for lists from small, but not large, image sets
- PMID: 20035843
- PMCID: PMC2830856
- DOI: 10.1016/j.beproc.2009.12.013
Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) show robust primacy and recency in memory for lists from small, but not large, image sets
Abstract
The combination of primacy and recency produces a U-shaped serial position curve typical of memory for lists. In humans, primacy is often thought to result from rehearsal, but there is little evidence for rehearsal in nonhumans. To further evaluate the possibility that rehearsal contributes to primacy in monkeys, we compared memory for lists of familiar stimuli (which may be easier to rehearse) to memory for unfamiliar stimuli (which are likely difficult to rehearse). Six rhesus monkeys saw lists of five images drawn from either large, medium, or small image sets. After presentation of each list, memory for one item was assessed using a serial probe recognition test. Across four experiments, we found robust primacy and recency with lists drawn from small and medium, but not large, image sets. This finding is consistent with the idea that familiar items are easier to rehearse and that rehearsal contributes to primacy, warranting further study of the possibility of rehearsal in monkeys. However, alternative interpretations are also viable and are discussed.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

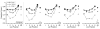
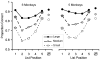
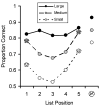
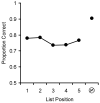
References
-
- Aron A, Aron E. Statistics for psychology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1999.
-
- Atkinson RC, Shiffrin RM. Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In: Spence KW, Spence JT, editors. The Psychology of Learning and Motivation: Advances in Research and Theory. Vol. 2. New York: Academic Press; 1968. pp. 89–195.
-
- Baddeley A. Working Memory. Science. 1992;255(5044):556–559. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley AD, Hitch G. The Recency Effect - Implicit Learning with Explicit Retrieval. Memory & Cognition. 1993;21(2):146–155. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley AD, Warrington EK. Amnesia and Distinction between Long-and Short-Term Memory. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior. 1970;9(2):176.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

