Pharmacological inhibition of BLT1 diminishes early abdominal aneurysm formation
- PMID: 20035940
- PMCID: PMC2862127
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.11.031
Pharmacological inhibition of BLT1 diminishes early abdominal aneurysm formation
Abstract
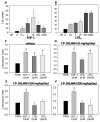
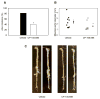
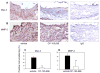
Leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)) is a pro-inflammatory lipid mediator generated by the enzymes 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) and LTA(4)-hydrolase. LTB(4) signals primarily through its G protein-coupled receptor BLT1, which is highly expressed on specific leukocyte subsets. Recent genetic studies in humans as well as knockout studies in mice have implicated the leukotriene synthesis pathway in several vascular pathologies. Here we tested the hypothesis that pharmacological inhibition of BLT1 diminishes abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) formation, a major complication associated with atherosclerotic vascular disease. Chow-fed Apoe(-/-) mice were treated with a 4-week infusion of Angiotensin II (AngII, 1000 ng/(kg min)) beginning at 10 weeks of age, in a well-established murine AAA model. Administration of the selective BLT1 antagonist CP-105,696 beginning simultaneously with AngII infusion reduced the incidence of AAA formation from 82% to 40% (p<0.05). There was a concordant reduction in maximal aortic diameter from 2.35 mm to 1.56 mm (p<0.05). While administration of the antagonist on day 14 after the onset of AngII infusion diminished lesional macrophage accumulation, it did not significantly alter the size of AAA by day 42. Thus, pharmacological inhibition of BLT1 may ultimately hold clinical promise, but early intervention may be critical.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibited aortic aneurysm formation in BLT1-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 1;179(1):691-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.691. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17579092
-
Blockade of the interaction of leukotriene b4 with its receptor prevents development of autoimmune uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Apr;47(4):1543-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1238. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16565390
-
Mas receptor deficiency augments angiotensin II-induced atherosclerosis and aortic aneurysm ruptures in hypercholesterolemic male mice.J Vasc Surg. 2019 Nov;70(5):1658-1668.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.11.045. Epub 2019 Mar 6. J Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30850299 Free PMC article.
-
Leukotriene B4 promotes neovascularization and macrophage recruitment in murine wet-type AMD models.JCI Insight. 2018 Sep 20;3(18):e96902. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.96902. eCollection 2018 Sep 20. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30232269 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestin-2 deficiency attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in mice.Circ Res. 2013 Apr 26;112(9):1219-29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.280399. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23524589 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):308-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25316652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 antagonism prevents experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 20;115(8):1907-1912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717906115. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29432192 Free PMC article.
-
5-Lipoxygenase pathway in experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Dec;34(12):2669-78. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304016. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25324573 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomic Profiling in Black and White Populations Reveals Novel Candidate Pathways in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Incident Heart Failure Specific to Black Adults.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2021 Jun;14(3):e003191. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.120.003191. Epub 2021 May 21. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2021. PMID: 34019435 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A pirinixic acid derivative (LP105) inhibits murine 5-lipoxygenase activity and attenuates vascular remodelling in a murine model of aortic aneurysm.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;163(8):1721-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01321.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21410457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Caterina R, Mazzone A, Giannessi D, et al. Leukotriene B4 production in human atherosclerotic plaques. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1988;47:S182–5. - PubMed
-
- Dwyer JH, Allayee H, Dwyer KM, et al. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase promoter genotype, dietary arachidonic acid, and atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:29–37. - PubMed
-
- Helgadottir A, Manolescu A, Helgason A, et al. A variant of the gene encoding leukotriene A4 hydrolase confers ethnicity-specific risk of myocardial infarction. Nat Genet. 2006;38:68–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

