T-helper 2 cells are essential for modulation of vascular repair by allogeneic endothelial cells
- PMID: 20036161
- PMCID: PMC2846227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2009.11.006
T-helper 2 cells are essential for modulation of vascular repair by allogeneic endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Endothelial cells (ECs) embedded within 3-dimensional matrices (MEEC) control lumenal inflammation and intimal hyperplasia when placed in the vascular adventitia. Matrix embedding alters endothelial immunogenicity in vitro. T-helper (Th) cell-driven host immunity is an impediment of allogeneic grafts. We aimed to identify if modulation of Th balance would affect immune compatibility and endothelial regulation of vascular repair in vivo.
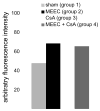
Methods: Pigs (n = 4/group) underwent carotid artery balloon injury and were left untreated (Group 1) or received perivascular porcine MEEC implants (Group 2), 12 days of cyclosporine A (CsA; Group 3), or MEEC and CsA (Group 4). Host immune reactivity was analyzed after 28 and 90 days.
Results: MEEC treatment induced formation of EC-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) G(1) antibodies (41 +/- 6 mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]) and differentiation of host splenocytes into Th2, but not Th1, cytokine-producing cells (interleukin [IL]-4, 242 +/- 102; IL-10, 273 +/- 114 number of spots). Concomitant CsA therapy reduced IgG(1) antibody frequency (25 +/- 2 MFI; p < 0.02) and Th2-cytokine producing splenocytes upon MEEC treatment (IL-4, 157 +/- 19; IL-10, 124 +/- 26 number of spots; p < 0.05). MEECs inhibited luminal occlusion 28 and 90 days after balloon injury (12 +/- 7%) vs untreated controls (68 +/- 14%; p < 0.001) but to a lesser extent with concomitant CsA treatment (34 +/- 13%; p < 0.02 vs Group 2).
Conclusions: MEECs do not induce a significant Th1-driven immune response but do enhance differentiation of splenocytes into cells producing Th2 cytokine. Reduction in this Th2 response reduces the vasoregulatory effects of allogeneic ECs after injury.
Figures
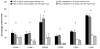
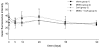
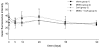
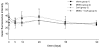



Similar articles
-
Fibrin glue containing fibroblast growth factor type 1 and heparin with autologous endothelial cells reduces intimal hyperplasia in a canine carotid artery balloon injury model.J Vasc Surg. 1997 May;25(5):840-8; discussion 848-9. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(97)70213-1. J Vasc Surg. 1997. PMID: 9152311
-
Matrix adherence of endothelial cells attenuates immune reactivity: induction of hyporesponsiveness in allo- and xenogeneic models.FASEB J. 2007 May;21(7):1515-26. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7051com. Epub 2007 Jan 30. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17264166
-
Endothelial implants inhibit intimal hyperplasia after porcine angioplasty.Circ Res. 1999 Mar 5;84(4):384-91. doi: 10.1161/01.res.84.4.384. Circ Res. 1999. PMID: 10066672
-
FTY720, an immunosuppressant that alters lymphocyte trafficking, abrogates chronic rejection in combination with cyclosporine A.Transplantation. 2003 Apr 15;75(7):945-52. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000058469.38572.10. Transplantation. 2003. PMID: 12698078
-
Species specialization in cytokine biology: is interleukin-4 central to the T(H)1-T(H)2 paradigm in swine?Dev Comp Immunol. 2009 Mar;33(3):344-52. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.06.014. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18761033 Review.
Cited by
-
Implantation of healthy matrix-embedded endothelial cells rescues dysfunctional endothelium and ischaemic tissue in liver engraftment.Gut. 2017 Jul;66(7):1297-1305. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310409. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Gut. 2017. PMID: 26851165 Free PMC article.
-
Substratum interactions determine immune response to allogeneic transplants of endothelial cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 8;13:946794. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.946794. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36003373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nabel EG. Biology of the impaired endothelium. The American journal of cardiology. 1991;68:6C–8C. - PubMed
-
- Methe H, Nugent HM, Groothuis A, Seifert P, Sayegh MH, Edelman ER. Matrix embedding alters the immune response against endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Circulation. 2005;112:I89–95. - PubMed
-
- Nugent HM, Edelman ER. Endothelial implants provide long-term control of vascular repair in a porcine model of arterial injury. The Journal of surgical research. 2001;99:228–34. - PubMed
-
- Nugent HM, Rogers C, Edelman ER. Endothelial implants inhibit intimal hyperplasia after porcine angioplasty. Circulation research. 1999;84:384–91. - PubMed
-
- Methe H, Edelman ER. Cell-matrix contact prevents recognition and damage of endothelial cells in states of heightened immunity. Circulation. 2006;114:I233–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

