Funny current provides a relatively modest contribution to spontaneous beating rate regulation of human and rabbit sinoatrial node cells
- PMID: 20036245
- PMCID: PMC2837765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.12.009
Funny current provides a relatively modest contribution to spontaneous beating rate regulation of human and rabbit sinoatrial node cells
Keywords: Na+/Ca2+ exchange current; action potentials; ion channels HCN4 hyperpolarization-activated current; pacemaker activity; sinoatrial node.
Figures
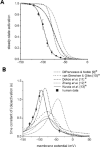
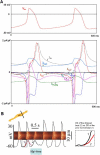
Comment on
-
Relative importance of funny current in human versus rabbit sinoatrial node.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Apr;48(4):799-801; author reply 802-3. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.09.020. Epub 2010 Jan 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20060834 No abstract available.
References
-
- Verkerk AO, Wilders R. Relative importance of funny current in human versus rabbit sinoatrial node. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2009 in press. - PubMed
-
- Yanagihara K, Irisawa H. Inward current activated during hyperpolarization in the rabbit sinoatrial node cell. Pflugers Arch. 1980;385:11–9. - PubMed
-
- Robinson RB, Siegelbaum SA. Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents: from molecules to physiological function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2003;65:453–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

