Hard and soft micro- and nanofabrication: An integrated approach to hydrogel-based biosensing and drug delivery
- PMID: 20036310
- PMCID: PMC2846451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.12.012
Hard and soft micro- and nanofabrication: An integrated approach to hydrogel-based biosensing and drug delivery
Abstract
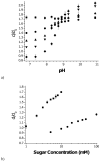
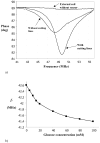
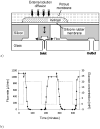
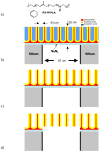
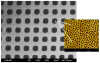
We review efforts to produce microfabricated glucose sensors and closed-loop insulin delivery systems. These devices function due to the swelling and shrinking of glucose-sensitive microgels that are incorporated into silicon-based microdevices. The glucose response of the hydrogel is due to incorporated phenylboronic acid (PBA) side chains. It is shown that in the presence of glucose, these polymers alter their swelling properties, either by ionization or by formation of glucose-mediated reversible crosslinks. Swelling pressures impinge on microdevice structures, leading either to a change in resonant frequency of a microcircuit, or valving action. Potential areas for future development and improvement are described. Finally, an asymmetric nano-microporous membrane, which may be integrated with the glucose-sensitive devices, is described. This membrane, formed using photolithography and block polymer assembly techniques, can be functionalized to enhance its biocompatibility and solute size selectivity. The work described here features the interplay of design considerations at the supramolecular, nano, and micro scales.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

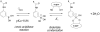





Similar articles
-
Top-down and bottom-up fabrication techniques for hydrogel based sensing and hormone delivery microdevices.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:232-5. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5332511. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19963454
-
pH and glucose dual-responsive phenylboronic acid hydrogels for smart insulin delivery.Soft Matter. 2024 Nov 13;20(44):8855-8865. doi: 10.1039/d4sm01004c. Soft Matter. 2024. PMID: 39474819
-
Hard and soft micromachining for BioMEMS: review of techniques and examples of applications in microfluidics and drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004 Feb 10;56(2):145-72. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2003.09.001. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004. PMID: 14741113 Review.
-
Phenylboronic Acid Appended Pyrene-Based Low-Molecular-Weight Injectable Hydrogel: Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Release.Chemistry. 2015 Aug 17;21(34):12042-52. doi: 10.1002/chem.201501170. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Chemistry. 2015. PMID: 26184777
-
Flow control with hydrogels.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004 Feb 10;56(2):199-210. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2003.08.013. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004. PMID: 14741116 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication of micropatterned polymeric nanowire arrays for high-resolution reagent localization and topographical cellular control.Nano Lett. 2015 Mar 11;15(3):1540-6. doi: 10.1021/nl503872p. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 25639724 Free PMC article.
-
Fully dissolved glucose-responsive insulin delivery system based on a self-immolative insulin prodrug and glucose oxidase.Chem Sci. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1039/d5sc02817e. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40836936 Free PMC article.
-
Can nanoparticles and nano‒protein interactions bring a bright future for insulin delivery?Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Mar;11(3):651-667. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.08.016. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33777673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Hydrogel-Based Ultrasonic Backscattering Wireless Biochemical Sensing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Nov 27;8:596370. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.596370. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33330426 Free PMC article.
-
Control of polymerization shrinkage and stress in nanogel-modified monomer and composite materials.Dent Mater. 2011 Jun;27(6):509-19. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Dent Mater. 2011. PMID: 21388669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flory PJ. Principles of Polymer Chemistry. Cornell University Press; 1953.
-
- Katchalsky A. Polyelectrolyte gels. Prog Biophys Chem. 1954;4:1–59.
-
- English A, Tanaka T, Edelman ER. Equilibrium and non-equilibrium phase transitions in copolymer polyelectrolyte hydrogels. J Chem Phys. 1997;107(5):1645–1654.
-
- Ricka J, Tanaka T. Swelling of ionic gels: Quantitative performance of the Donnan theory. Macromolecules. 1984;17:2916–2921.
-
- Firestone BA, Siegel RA. pH, salt, and buffer dependent swelling in ionizable copolymer gels: Tests of the ideal Donnan equilibrium theory. J Biomat Sci Polym Ed. 1994;5:433–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

