Cortical sources of the respiratory-related evoked potential
- PMID: 20036344
- PMCID: PMC2819639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2009.12.006
Cortical sources of the respiratory-related evoked potential
Abstract
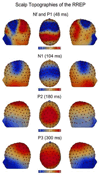
The respiratory-related evoked potential (RREP) is increasingly used to study the neural processing of respiratory signals. However, little is known about the cortical origins of early (Nf, P1, N1) and later RREP components (P2, P3). By using high-density EEG, we studied cortical sources of RREP components elicited by short inspiratory occlusions in 18 healthy volunteers (6 female, mean age 20.0+/-1.8 years). Topographical maps for Nf and P1 showed bilateral maximum EEG voltages over the frontal and centro-parietal cortex, respectively. Cortical source analyses (minimum-norm estimates) in addition to topographical maps demonstrated bilateral sensorimotor cortex origins for N1 and P2 which were paralleled by an additional frontal cortex source (p's<0.05). The source of the P3 was located at the parietal cortex (p<0.05). The results support previous findings on the cortical sources of early RREP components Nf, P1 and N1 and demonstrate the cortical sources of later RREP components P2 and P3.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Respiratory-related evoked potential measurements using high-density electroencephalography.Clin Neurophysiol. 2011 Apr;122(4):815-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2010.10.031. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21067971 Free PMC article.
-
The respiratory-related evoked potential: effects of attention and occlusion duration.Psychophysiology. 2000 May;37(3):310-8. Psychophysiology. 2000. PMID: 10860409 Clinical Trial.
-
The test-retest reliability of the respiratory-related evoked potential.Biol Psychol. 2021 Jul;163:108133. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2021.108133. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Biol Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34118356 Review.
-
The impact of emotion on respiratory-related evoked potentials.Psychophysiology. 2010 May 1;47(3):579-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00956.x. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Psychophysiology. 2010. PMID: 20070570 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory related evoked potential measures of cerebral cortical respiratory information processing.Biol Psychol. 2010 Apr;84(1):4-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.02.009. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Biol Psychol. 2010. PMID: 20188140 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of spiking and bursting pacemakers in the neuronal control of breathing.J Biol Phys. 2011 Jun;37(3):241-61. doi: 10.1007/s10867-011-9214-z. Epub 2011 Mar 22. J Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 22654176 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) around the World.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 10;23(8):3866. doi: 10.3390/s23083866. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112214 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory modulation of startle eye blink: a new approach to assess afferent signals from the respiratory system.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Nov 19;371(1708):20160019. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0019. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 28080976 Free PMC article.
-
Interoception and stress.Front Psychol. 2015 Jul 20;6:993. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00993. eCollection 2015. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26257668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Autonomic Network: Synchrony Between Slow Rhythms of Pulse and Brain Resting State Is Associated with Personality and Emotions.Cereb Cortex. 2018 Sep 1;28(9):3356-3371. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy144. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 29955858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan PS, Davenport PW. Respiratory Related Evoked Potential Measures of Cerebral Cortical Respiratory Information Processing. Biol. Psych. in press. - PubMed
-
- Davenport PW, Colrain IM, Hill PM. Scalp topography of the short-latency components of the respiratory-related evoked potential in children. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996;80:1785–1791. - PubMed
-
- Davenport PW, Friedman WA, Thompson FJ, Franzen O. Respiratory-related cortical potentials evoked by inspiratory occlusion in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986;60:1843–1848. - PubMed
-
- Davenport PW, Vovk A. Cortical and subcortical central neural pathways in respiratory sensations. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009;167:72–86. - PubMed
-
- Harver A, Squires N, Bloch-Salisbury E, Katkin E. Event-related potentials to airway occlusion in young and old subjects. Psychophysiology. 1995;32:121–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

