Zebrafish fetal alcohol syndrome model: effects of ethanol are rescued by retinoic acid supplement
- PMID: 20036484
- PMCID: PMC2889201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.03.004
Zebrafish fetal alcohol syndrome model: effects of ethanol are rescued by retinoic acid supplement
Abstract
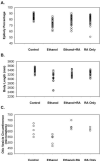
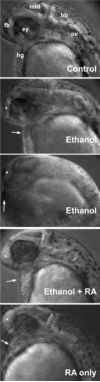
This study was designed to develop a zebrafish experimental model to examine defects in retinoic acid (RA) signaling caused by embryonic ethanol exposure. RA deficiency may be a causative factor leading to a spectrum of birth defects classified as fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD). Experimental support for this hypothesis using Xenopus showed that effects of treatment with ethanol could be partially rescued by adding retinoids during ethanol treatment. Previous studies show that treating zebrafish embryos during gastrulation and somitogenesis stages with a pathophysiological concentration of ethanol (100mM) produces effects that are characteristic features of FASD. We found that treating zebrafish embryos with RA at a low concentration (10(-9)M) and 100mM ethanol during gastrulation and somitogenesis stages significantly rescued a spectrum of defects produced by treating embryos with 100mM ethanol alone. The rescued phenotype that we observed was quantitatively more similar to embryos treated with 10(-9)M RA alone (RA toxicity) than to untreated or 100mM ethanol-treated embryos. RA rescued defects caused by 100mM ethanol treatment during gastrulation and somitogenesis stages that include early gastrulation cell movements (anterior-posterior axis), craniofacial cartilage formation, and ear development. Morphological evidence also suggests that other characteristic features of FASD (e.g., neural axis patterning) are rescued by RA supplement.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Begemann G, Meyer A. Hindbrain patterning revisited: timing and effects of retinoic acid signalling. Bioessays. 2001;23:981–986. - PubMed
-
- Begemann G, Schilling TF, Rauch GJ, Geisler R, Ingham PW. The zebrafish neckless mutation reveals a requirement for raldh2 in mesodermal signals that pattern the hindbrain. Development. 2001;128:3081–3094. - PubMed
-
- Blader P, Strahle U. Ethanol impairs migration of the prechordal plate in the zebrafish embryo. Dev. Biol. 1998;201:185–201. - PubMed
-
- Bradfield JY, West JR, Maier SE. Uptake and elimination of ethanol by young zebrafish embryos. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2006;28:629–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

