The human carnitine transporter SLC22A16 mediates high affinity uptake of the anticancer polyamine analogue bleomycin-A5
- PMID: 20037140
- PMCID: PMC2825423
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.046151
The human carnitine transporter SLC22A16 mediates high affinity uptake of the anticancer polyamine analogue bleomycin-A5
Abstract
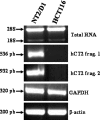
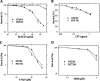
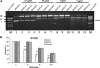
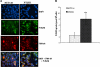
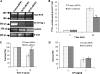
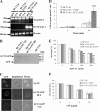
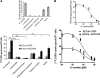
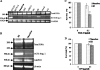
Bleomycin is used in combination with other antineoplastic agents to effectively treat lymphomas, testicular carcinomas, and squamous cell carcinomas of the cervix, head, and neck. However, resistance to bleomycin remains a persistent limitation in exploiting the full therapeutic benefit of the drug with other types of cancers. Previously, we documented that the Saccharomyces cerevisiae L-carnitine transporter Agp2 is responsible for the high affinity uptake of polyamines and of the polyamine analogue bleomycin-A5. Herein, we document that the human L-carnitine transporter hCT2 encoded by the SLC22A16 gene is involved in bleomycin-A5 uptake, as well as polyamines. We show that NT2/D1 human testicular cancer cells, which highly express hCT2, are extremely sensitive to bleomycin-A5, whereas HCT116 human colon carcinoma cells devoid of detectable hCT2 expression or MCF-7 human breast cancer cells that only weakly express the permease showed striking resistance to the drug. NT2/D1 cells accumulated fluorescein-labeled bleomycin-A5 to substantially higher levels than HCT116 cells. Moreover, L-carnitine protected NT2/D1 cells from the lethal effects of bleomycin-A5 by preventing its influx, and siRNA targeted to hCT2 induced resistance to bleomycin-A5-dependent genotoxicity. Furthermore, hCT2 overexpression induced by transient transfection of a functional hCT2-GFP fusion protein sensitized HCT116 cells to bleomycin-A5. Collectively, our data strongly suggest that hCT2 can mediate bleomycin-A5 and polyamine uptake, and that the rate of bleomycin-A5 accumulation may account for the differential response to the drug in patients.
Figures
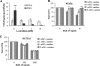
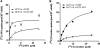
References
-
- Umezawa H. (1965) Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 5, 1079–1085 - PubMed
-
- Umezawa H., Maeda K., Takeuchi T., Okami Y. (1966) J. Antibiot. 19, 200–209 - PubMed
-
- Umezawa H. (1971) Pure. Appl. Chem. 28, 665–680 - PubMed
-
- Giloni L., Takeshita M., Johnson F., Iden C., Grollman A. P. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 8608–8615 - PubMed
-
- Steighner R. J., Povirk L. F. (1990) Mutat. Res. 240, 93–100 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

