Inhibition of ERK1/2 and activation of liver X receptor synergistically induce macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux
- PMID: 20037141
- PMCID: PMC2825427
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.073601
Inhibition of ERK1/2 and activation of liver X receptor synergistically induce macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux
Abstract
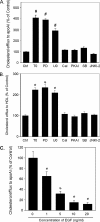
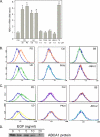
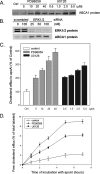
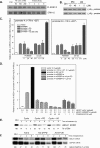
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), a molecule mediating free cholesterol efflux from peripheral tissues to apoAI and high density lipoprotein (HDL), inhibits the formation of lipid-laden macrophage/foam cells and the development of atherosclerosis. ERK1/2 are important signaling molecules regulating cellular growth and differentiation. The ERK1/2 signaling pathway is implicated in cardiac development and hypertrophy. However, the role of ERK1/2 in the development of atherosclerosis, particularly in macrophage cholesterol homeostasis, is unknown. In this study, we investigated the effects of ERK1/2 activity on macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux. Compared with a minor effect by inhibition of other kinases, inhibition of ERK1/2 significantly increased macrophage cholesterol efflux to apoAI and HDL. In contrast, activation of ERK1/2 reduced macrophage cholesterol efflux and ABCA1 expression. The increased cholesterol efflux by ERK1/2 inhibitors was associated with the increased ABCA1 levels and the binding of apoAI to cells. The increased ABCA1 by ERK1/2 inhibitors was due to increased ABCA1 mRNA and protein stability. The induction of ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux by ERK1/2 inhibitors was concentration-dependent. The mechanism study indicated that activation of liver X receptor (LXR) had little effect on ERK1/2 expression and activation. ERK1/2 inhibitors had no effect on macrophage LXRalpha/beta expression, whereas they did not influence the activation or the inhibition of the ABCA1 promoter by LXR or sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP). However, inhibition of ERK1/2 and activation of LXR synergistically induced macrophage cholesterol efflux and ABCA1 expression. Our data suggest that ERK1/2 activity can play an important role in macrophage cholesterol trafficking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors induce macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux-an LXR-dependent mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1831(6):1134-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23466610
-
Genetic deletion of low density lipoprotein receptor impairs sterol-induced mouse macrophage ABCA1 expression. A new SREBP1-dependent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 25;283(4):2129-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706636200. Epub 2007 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18029360
-
Atorvastatin inhibits ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophages by an LXR-dependent pathway.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008 Apr;51(4):388-95. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318167141f. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18427282
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
-
ABCA1 and nascent HDL biogenesis.Biofactors. 2014 Nov-Dec;40(6):547-54. doi: 10.1002/biof.1187. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Biofactors. 2014. PMID: 25359426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription of liver X receptor is down-regulated by 15-deoxy-Δ(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2) through oxidative stress in human neutrophils.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e42195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042195. Epub 2012 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23115616 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of liver X receptor inhibits OCT2-mediated organic cation transport in renal proximal tubular cells.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Nov;469(11):1471-1481. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2033-8. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28741179
-
Participation of ABCA1 Transporter in Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 24;22(7):3334. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073334. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tumor suppressor TERE1 (UBIAD1) prenyltransferase regulates the elevated cholesterol phenotype in castration resistant prostate cancer by controlling a program of ligand dependent SXR target genes.Oncotarget. 2013 Jul;4(7):1075-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1103. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23919967 Free PMC article.
-
MEK1/2 inhibitor inhibits neointima formation by activating miR-126-3p/ C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12)/C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):11214-11227. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2063496. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35485167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arora S., Nicholls S. J. (2008) Drugs Today 44, 711–718 - PubMed
-
- de Villiers W. J., Smart E. J. (1999) J. Leukocyte Biol. 66, 740–746 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H., Kurihara Y., Takeya M., Kamada N., Kataoka M., Jishage K., Ueda O., Sakaguchi H., Higashi T., Suzuki T., Takashima Y., Kawabe Y., Cynshi O., Wada Y., Honda M., Kurihara H., Aburatani H., Doi T., Matsumoto A., Azuma S., Noda T., Toyoda Y., Itakura H., Yazaki Y., Kodama T. (1997) Nature 386, 292–296 - PubMed
-
- Braun A., Trigatti B. L., Post M. J., Sato K., Simons M., Edelberg J. M., Rosenberg R. D., Schrenzel M., Krieger M. (2002) Circ. Res. 90, 270–276 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

