Effects of phosphorus supply on growth, phosphate concentration and cluster-root formation in three Lupinus species
- PMID: 20037142
- PMCID: PMC2826247
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcp297
Effects of phosphorus supply on growth, phosphate concentration and cluster-root formation in three Lupinus species
Abstract
Background and aims: In some lupin species, phosphate deficiency induces cluster-root formation, which enhances P uptake by increasing root surface area and, more importantly, the release of root exudates which enhances P availability.
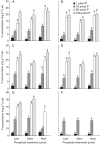
Methods: Three species of Lupinus, L. albus, L. atlanticus and L. micranthus, with inherently different relative growth rates were cultivated under hydroponics in a greenhouse at four phosphate concentrations (1, 10, 50 and 150 microm) to compare the role of internal P in regulating cluster-root formation.
Key results: The highest growth rate was observed in L. atlanticus, followed by L. albus and L. micranthus. At 1 microm P, cluster-root formation was markedly induced in all three species. The highest P uptake and accumulation was observed in L. micranthus, followed by L. atlanticus and then L. albus. Inhibition of cluster-root formation was severe at 10 microm P in L. atlanticus, but occurred stepwise with increasing P concentration in the root medium in L. albus.
Conclusions: In L. atlanticus and L. albus cluster-root formation was suppressed by P treatments above 10 microm, indicating a P-inducible regulating system for cluster-root formation, as expected. By contrast, production of cluster roots in L. micranthus, in spite of a high internal P concentration, indicated a lower sensitivity to P status, which allowed P-toxicity symptoms to develop.
Figures




References
-
- Bolland MDA, Siddique KHM, Loss SP, Baker MJ. Comparing responses of grain legumes, wheat and canola to applications of superphosphate. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems. 1999;53:157–175.
-
- Cordell D, Drangert J-O, White S. The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change. 2009;19:292–305.
-
- Curtin D, Syers JK, Bolan NS. Phosphate sorption by soil in relation to exchangeable cation composition and pH. Australian Journal of Soil Research. 1993;31:137–149.
-
- Fujii H, Chiou T, Lin S, Aung K, Zhu J. A miRNA involved in phosphate-starvation response in Arabidopsis. Current Biology. 2005;15:2038–2043. - PubMed

