Cardio-renal syndromes: report from the consensus conference of the acute dialysis quality initiative
- PMID: 20037146
- PMCID: PMC2838681
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp507
Cardio-renal syndromes: report from the consensus conference of the acute dialysis quality initiative
Abstract
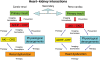
A consensus conference on cardio-renal syndromes (CRS) was held in Venice Italy, in September 2008 under the auspices of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). The following topics were matter of discussion after a systematic literature review and the appraisal of the best available evidence: definition/classification system; epidemiology; diagnostic criteria and biomarkers; prevention/protection strategies; management and therapy. The umbrella term CRS was used to identify a disorder of the heart and kidneys whereby acute or chronic dysfunction in one organ may induce acute or chronic dysfunction in the other organ. Different syndromes were identified and classified into five subtypes. Acute CRS (type 1): acute worsening of heart function (AHF-ACS) leading to kidney injury and/or dysfunction. Chronic cardio-renal syndrome (type 2): chronic abnormalities in heart function (CHF-CHD) leading to kidney injury and/or dysfunction. Acute reno-cardiac syndrome (type 3): acute worsening of kidney function (AKI) leading to heart injury and/or dysfunction. Chronic reno-cardiac syndrome (type 4): chronic kidney disease leading to heart injury, disease, and/or dysfunction. Secondary CRS (type 5): systemic conditions leading to simultaneous injury and/or dysfunction of heart and kidney. Consensus statements concerning epidemiology, diagnosis, prevention, and management strategies are discussed in the paper for each of the syndromes.
Figures

References
-
- Heywood JT. The cardiorenal syndrome: lessons from the ADHERE database and treatment options. Heart Fail Rev. 2004;9:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Forman DE, Butler J, Wang Y, Abraham WT, O'Connor CM, Gottlieb SS, Loh E, Massie BM, Rich MW, Stevenson LW, Young JB, Krumholz HM. Incidence, predictors at admission, and impact of worsening renal function among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C, House AA, Haapio M. Cardiorenal syndrome: refining the definition of a complex symbiosis gone wrong. Intensive Care Med. 2008;34:957–962. - PubMed
-
- Liang KV, Williams AW, Greene EL, Redfield MM. Acute decompensated heart failure and the cardiorenal syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(Suppl. 1):S75–S88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

