Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: predictive factors, prognostic value, and comparison with surgical aortic valve replacement
- PMID: 20037180
- PMCID: PMC2848323
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp552
Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: predictive factors, prognostic value, and comparison with surgical aortic valve replacement
Abstract
Aims: Very few data exist on the occurrence of acute kidney injury (AKI) associated with transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). The objectives of the present study were (i) to determine the incidence, predictive factors, and prognostic value of AKI following TAVI, and (ii) to compare the occurrence of AKI in TAVI vs. surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in patients with pre-procedural chronic kidney disease (CKD).
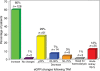
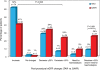
Methods and results: A total of 213 patients (mean age 82 +/- 8 years) undergoing TAVI for the treatment of severe aortic stenosis were included in the study. Acute kidney injury was defined as a reduction of >25% in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) within 48 h following the procedure or the need for haemodialysis during index hospitalization. Those patients with pre-procedural CKD (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m(2), n = 119) were compared with 104 contemporary patients with CKD who underwent isolated SAVR. The incidence of AKI following TAVI was 11.7%, with 1.4% of the patients requiring haemodialysis. Predictive factors of AKI were hypertension (OR: 4.66; 95% CI: 1.04-20.87), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (OR: 2.64, 95% CI: 1.10-6.36), and peri-operative blood transfusion (OR: 3.47, 95% CI: 1.30-9.29). Twenty-one patients (9.8%) died during index hospitalization, and the logistic EuroSCORE (OR: 1.03 for each increase of 1%; 95% CI: 1.01-1.06) and occurrence of AKI (OR: 4.14, 95% CI: 1.42-12.13) were identified as independent predictors of postoperative mortality. Patients with CKD who underwent TAVI were older, had a higher logistic EuroSCORE and lower pre-procedural eGFR values compared with those who underwent SAVR (P < 0.0001 for all). The incidence of AKI was lower (P = 0.001; P = 0.014 after propensity score adjustment) in CKD patients who underwent TAVI (9.2%, need for haemodialysis: 2.5%) compared with those who underwent SAVR (25.9%, need for haemodialysis: 8.7%).
Conclusion: Acute kidney injury occurred in 11.7% of the patients following TAVI and was associated with a greater than four-fold increase in the risk of postoperative mortality. Hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and blood transfusion were predictive factors of AKI. In those patients with pre-procedural CKD, TAVI was associated with a significant reduction of AKI compared with SAVR.
Figures
References
-
- Rosner MH, Okusa MD. Acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:19–32. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Levy EM, Hammermeister KE, Grover F, Daley J. Independent association between acute renal failure and mortality following cardiac surgery. Am J Med. 1998;104:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Loef BG, Epema AH, Smilde TD, Henning RH, Ebels T, Navis G, Stegeman CA. Immediate postoperative renal function deterioration in cardiac surgical patients predicts in-hospital mortality and long-term survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Karkouti K, Wijeysundera DN, Yau TM, Callum JL, Cheng DC, Crowther M, Dupuis JY, Fremes SE, Kent B, Laflamme C, Lamy A, Legare JF, Mazer CD, McCluskey SA, Rubens FD, Sawchuk C, Beattie WS. Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: focus on modifiable risk factors. Circulation. 2009;119:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Cribier A, Eltchaninoff H, Tron C, Bauer F, Agatiello C, Nercolini D, Tapiero S, Litzler PY, Bessou JP, Babaliaros V. Treatment of calcific aortic stenosis with the percutaneous heart valve: mid-term follow-up from the initial feasibility studies: the French experience. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:1214–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

