APC-targeted RAA1 degradation mediates the cell cycle and root development in plants
- PMID: 20037474
- PMCID: PMC2881264
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.5.3.10661
APC-targeted RAA1 degradation mediates the cell cycle and root development in plants
Abstract
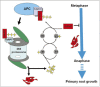
Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system is necessary for a normal cell cycle. As compared with knowledge of the mechanism in animals and yeast, that in plants is less known. Here we summarize research into the regulatory mechanism of protein degradation in the cell cycle in plants. Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC), in the E3 family of enzymes, plays an important role in maintaining normal mitosis. APC activation and substrate specificity is determined by its activators, which can recognize the destruction box (D-box) in APC target proteins. Oryza sativa root architecture-associated 1 (OsRAA1) with GTP-binding activity was originally cloned from rice. Overexpression of of OsRAA1 inhibits the growth of primary roots in rice. Knockdown lines showed reduced height of seedlings because of abnormal cell division. OsRAA1 transgenic rice and fission yeast show a higher proportion of metaphase cells than that of controls, which suggests a blocked transition from metaphase to anaphase during mitosis. OsRAA1 co-localizes with spindle tubulin. It contains the D-box motif and interacts with OsRPT4 of the regulatory particle of 26S proteasome. OsRAA1 may be a cell cycle inhibitor that can be degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and its disruption is necessary for the transition from metaphase to anaphase during root growth in rice.
Figures
References
-
- Hellmann H, Estelle M. Plant development: regulation by protein degradation. Science. 2002;297:793–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
