HIF-1alpha links beta-adrenoceptor agonists and pancreatic cancer cells under normoxic condition
- PMID: 20037603
- PMCID: PMC4002695
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.181
HIF-1alpha links beta-adrenoceptor agonists and pancreatic cancer cells under normoxic condition
Abstract
Aim: To examine whether beta-adrenoceptor (beta-AR) agonists can induce hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha accumulation which then up-regulate the expression of its target genes in pancreatic cancer cells at normoxia, and to further elucidate the mechanism involved.
Methods: Pulse-chase assay, RT-PCR, and Western blot were employed to detect the effects of beta-AR agonists and antagonists, siRNA as well as several inhibitors of signal transduction pathways on MIA PaCa2 and BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells.
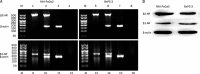
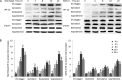
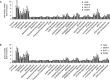
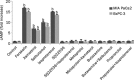
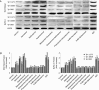
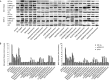
Results: Treatment of pancreatic cancer cell lines with beta-AR agonists led to accumulation of HIF-1alpha and then up-regulated expression of its target genes independently of oxygen levels. The induction was partly or completely inhibited not only by beta-AR antagonists but also by inhibitors of PKA transduction pathways and by siHIF-1alpha. Both beta1-AR and beta2-AR agonists produced the above-mentioned effects, but beta2-AR agonist was more potent.
Conclusion: Activation of beta-AR receptor transactivates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and then elicits Akt and ERK1/2 in a PKA-dependent manner, which together up-regulate levels of HIF-1alpha and downstream target genes independently of oxygen level. Our data suggest a novel mechanism in pancreatic cancer cells that links beta-AR and HIF-1alpha signaling under normoxic conditions, with implications for the control of glucose transport, angiogenesis and metastasis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha signal pathways increases resistance to apoptosis by up-regulating survivin gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):25903-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603414200. Epub 2006 Jul 17. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16847054 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cigarette smoke-mediated mucin expression by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α via epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling pathways.J Appl Toxicol. 2012 Apr;32(4):282-92. doi: 10.1002/jat.1679. Epub 2011 May 4. J Appl Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 21544845
-
Hypoxia-independent overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha as an early change in mouse hepatocarcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 1;66(23):11263-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1699. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17145871
-
Effects of YC-1 on hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in hypoxic human bladder transitional carcinoma cell line T24 cells.Urol Int. 2012;88(1):95-101. doi: 10.1159/000331881. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Urol Int. 2012. PMID: 22041818
-
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas.Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jan 26;29(1):71-91. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0032. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28822229 Review.
Cited by
-
S100a9 inhibits Atg9a transcription and participates in suppression of autophagy in cardiomyocytes induced by β1-adrenoceptor autoantibodies.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Sep 18;28(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00486-1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37723445 Free PMC article.
-
β2-AR-HIF-1α: a novel regulatory axis for stress-induced pancreatic tumor growth and angiogenesis.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Jul;13(6):1023-34. doi: 10.2174/15665240113139990055. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23745588 Free PMC article.
-
β2-adrenoceptor blockage induces G1/S phase arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via Ras/Akt/NFκB pathway.Mol Cancer. 2011 Nov 26;10:146. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-146. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22118662 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of perineural invasion, hypoxia and desmoplasia in pancreatic cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(17):2395-403. doi: 10.2174/13816128112092395. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22372500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine in Gastric Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 18;22(4):2042. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042042. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM, Takahashi R, Lu CH, et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med. 2006;12:939–44. - PubMed
-
- Audet M, Bouvier M. Insights into signaling from the β2-adrenergic receptor structure. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:397–403. - PubMed
-
- Thaker PH, Lutgendorf SK, Sood AK. The neuroendocrine impact of chronic stress on cancer. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:430–3. - PubMed
-
- Weddle DL, Tithoff P, Williams M, Schuller HM. β-Adrenergic growth regulation of human cancer cell lines derived from pancreatic ductal carcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:473–9. - PubMed
-
- Askari MD, Tsao MS, Schuller HM. The tobacco-specific carcinogen, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone stimulates proliferation of immortalized human pancreatic duct epithelia through β-adrenergic transactivation of EGF receptors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005;131:639–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

