Telomere length in human adults and high level natural background radiation
- PMID: 20037654
- PMCID: PMC2793520
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008440
Telomere length in human adults and high level natural background radiation
Abstract
Background: Telomere length is considered as a biomarker of aging, stress, cancer. It has been associated with many chronic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes. Although, telomere shortening due to ionizing radiation has been reported in vitro, no in vivo data is available on natural background radiation and its effect on telomere length.
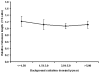
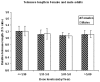
Methodology/principal findings: The present investigation is an attempt to determine the telomere length among human adults residing in high level natural radiation areas (HLNRA) and the adjacent normal level radiation areas (NLNRA) of Kerala coast in Southwest India. Genomic DNA was isolated from the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 310 individuals (HLNRA: N = 233 and NLNRA: N = 77). Telomere length was determined using real time q-PCR. Both telomere (T) and single copy gene (S) specific primers were used to calculate the relative T/S and expressed as the relative telomere length. The telomere length was determined to be 1.22+/-0.15, 1.12+/-0.15, 1.08+/-0.08, 1.12+/-0.11, respectively, among the four dose groups (</=1.50, 1.51-3.00, 3.01-5.00 and >5.00 mGy per year), which did not show any dose response. The results suggested that the high level natural chronic radiation did not have significant effect on telomere length among young adult population living in HLNRA, which is indicative of better repair of telomeric ends. No significant difference in telomere length was observed between male and female individuals. In the present investigation, although the determination of telomere length was studied among the adults with an age group between 18 to 40 years (mean maternal age: 26.10+/-4.49), a negative correlation was observed with respect to age. However, inter-individual variation was (0.81-1.68) was clearly observed.
Conclusions/significance: In this preliminary investigation, we conclude that elevated level of natural background radiation has no significant effect on telomere length among the adult population residing in HLNRAs of Kerala coast. To our knowledge, this is the first report from HLNRAs of the world where telomere length was determined on human adults. However, more samples from each background dose group and samples from older population need to be studied to derive firm conclusions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of natural chronic low dose radiation exposure on telomere length and transcriptional response of shelterin complex in individuals residing in Kerala coast, India.Mutat Res. 2022 Jul-Dec;825:111797. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2022.111797. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Mutat Res. 2022. PMID: 36116241
-
No evidence of telomere length attrition in newborns from high level natural background radiation areas in Kerala coast, south west India.Int J Radiat Biol. 2012 Sep;88(9):642-7. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2012.699135. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Int J Radiat Biol. 2012. PMID: 22668000
-
Non-linear dose response of DNA double strand breaks in response to chronic low dose radiation in individuals from high level natural radiation areas of Kerala coast.Genes Environ. 2023 May 1;45(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s41021-023-00273-6. Genes Environ. 2023. PMID: 37127760 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient repair of DNA double strand breaks in individuals from high level natural radiation areas of Kerala coast, south-west India.Mutat Res. 2017 Dec;806:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28963924
-
[Telomere shortening is the main mechanism of natural and radiation aging].Radiats Biol Radioecol. 2010 May-Jun;50(3):269-75. Radiats Biol Radioecol. 2010. PMID: 20734798 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Low dose rate γ-irradiation protects fruit fly chromosomes from double strand breaks and telomere fusions by reducing the esi-RNA biogenesis factor Loquacious.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 3;5(1):905. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03885-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36057690 Free PMC article.
-
Space Medicine: Why Do Recently Published Papers about Telomere Length Alterations Increase our Uncertainty Rather than Reduce it?J Biomed Phys Eng. 2021 Feb 1;11(1):103-108. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2005-1115. eCollection 2021 Feb. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2021. PMID: 33564645 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of alternative lengthening of telomeres by telomere quantitative PCR.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):e34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks781. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 22923525 Free PMC article.
-
Annual space weather fluctuations and telomere length dynamics in a longitudinal cohort of older men: the Normative Aging Study.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2024 Nov;34(6):1072-1080. doi: 10.1038/s41370-023-00616-z. Epub 2023 Dec 8. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38066331
-
Study of stillbirth and major congenital anomaly among newborns in the high-level natural radiation areas of Kerala, India.J Community Genet. 2013 Jan;4(1):21-31. doi: 10.1007/s12687-012-0113-1. Epub 2012 Aug 9. J Community Genet. 2013. PMID: 22875746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- George KP, Sundaram K, Mistry KB, Gopal-Ayengar AR. Investigations on human populations residing in high background radiation areas of Kerala and adjoining regions. Reprint from “Biological and environmental effects of low level radiation.”. 1976. Vol. II, IAEA, Vienna, SM - 202/703:325–329.
-
- Bharatwal DS, Vaze GH. Radiation dose measurements in the monazite areas of Kerala state in India. In: proceedings of the 2nd UN International conference on Peaceful uses of Atomic energy. United Nations, NewYork. 1958;23:156.
-
- Sunta CM. Sohrabi M, Ahmed JU, Durani SA, editors. A review of the studies of high background areas of the S-W coast of India. Proceedings of the International conference on high levels of natural radiation, Atomic Energy Organization of Iran, Tehran. 1993.
-
- Thampi MV, Cheriyan VD, Jaikrishan G, Das B, Kurien CJ, et al. Investigations on the health effects of human population residing in the high level natural radiation areas in Kerala in the southwest coast of India. International Congress Series. 2005;1276:8–12.
-
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiations (UNSCEAR) Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation Annex B Exposures from Natural Radiation Sources (New York: United Nations). 2000.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

