Toward engineering synthetic microbial metabolism
- PMID: 20037734
- PMCID: PMC2796345
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/459760
Toward engineering synthetic microbial metabolism
Abstract
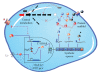
The generation of well-characterized parts and the formulation of biological design principles in synthetic biology are laying the foundation for more complex and advanced microbial metabolic engineering. Improvements in de novo DNA synthesis and codon-optimization alone are already contributing to the manufacturing of pathway enzymes with improved or novel function. Further development of analytical and computer-aided design tools should accelerate the forward engineering of precisely regulated synthetic pathways by providing a standard framework for the predictable design of biological systems from well-characterized parts. In this review we discuss the current state of synthetic biology within a four-stage framework (design, modeling, synthesis, analysis) and highlight areas requiring further advancement to facilitate true engineering of synthetic microbial metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A perspective of synthetic biology: assembling building blocks for novel functions.Biotechnol J. 2006 Jun;1(6):690-9. doi: 10.1002/biot.200600019. Biotechnol J. 2006. PMID: 16892318 Review.
-
De novo biosynthetic pathways: rational design of microbial chemical factories.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2008 Oct;19(5):468-74. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2008.07.009. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18725289 Review.
-
Setting the standard in synthetic biology.Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Jul;26(7):771-4. doi: 10.1038/nbt0708-771. Nat Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18612298 No abstract available.
-
Computational design of synthetic gene circuits with composable parts.Bioinformatics. 2008 Sep 1;24(17):1903-10. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn330. Epub 2008 Jun 25. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18579565
-
Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices.Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Jul;26(7):787-93. doi: 10.1038/nbt1413. Nat Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18612302
Cited by
-
Generating in vivo cloning vectors for parallel cloning of large gene clusters by homologous recombination.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e79979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079979. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244585 Free PMC article.
-
Designing novel cellulase systems through agent-based modeling and global sensitivity analysis.Bioengineered. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):243-53. doi: 10.4161/bioe.29160. Epub 2014 May 15. Bioengineered. 2014. PMID: 24830736 Free PMC article.
-
Circular polymerase extension cloning for high-throughput cloning of complex and combinatorial DNA libraries.Nat Protoc. 2011 Feb;6(2):242-51. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.181. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Nat Protoc. 2011. PMID: 21293463
-
Enhancing E. coli tolerance towards oxidative stress via engineering its global regulator cAMP receptor protein (CRP).PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051179. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251448 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic relationships between intron content and codon usage bias of genes in three mosquito species: functional and evolutionary implications.Evol Appl. 2013 Nov;6(7):1079-89. doi: 10.1111/eva.12088. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Evol Appl. 2013. PMID: 24187589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chin JW. Modular approaches to expanding the functions of living matter. Nature Chemical Biology. 2006;2(6):304–311. - PubMed
-
- Endy D. Foundations for engineering biology. Nature. 2005;438(7067):449–453. - PubMed
-
- Keasling JD. Synthetic biology for synthetic chemistry. ACS Chemical Biology. 2008;3(1):64–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

