Amelogenin nanoparticles in suspension: deviations from spherical shape and pH-dependent aggregation
- PMID: 20038137
- PMCID: PMC2817559
- DOI: 10.1021/bm900983b
Amelogenin nanoparticles in suspension: deviations from spherical shape and pH-dependent aggregation
Abstract
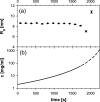
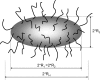
It is well-known that amelogenin self-assembles to form nanoparticles, usually referred to as amelogenin nanospheres, despite the fact that not much is known about their actual shape in solution. In the current paper, we combine SAXS and DLS to study the three-dimensional shape of the recombinant amelogenins rP172 and rM179. Our results show for the first time that amelogenins build oblate nanoparticles in suspension using experimental approaches that do not require the proteins to be in contact with a support material surface. The SAXS studies give evidence for the existence of isolated amelogenin nano-oblates with aspect ratios in the range of 0.45-0.5 at pH values higher than pH 7.2 and show an aggregation of these nano-oblates at lower pH values. The role of the observed oblate shape in the formation of chain-like structures at physiological conditions is discussed as a key factor in the biomineralization of dental enamel.
Figures



References
-
- Fincham A. G.; Moradian-Oldak J.; Simmer J. P. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 126 (3), 270–299. - PubMed
-
- Paine M. L.; White S. N.; Luo W.; Fong H.; Sarikaya M.; Snead M. L. Matrix Biol. 2001, 20 (5−6), 273–292. - PubMed
-
- Margolis H. C.; Beniash E.; Fowler C. E. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85 (9), 775–793. - PubMed
-
- Zeichner-David M. Matrix Biol. 2001, 20 (5−6), 307–316. - PubMed
-
- Aoba T.; Moreno E. C. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1987, 41 (2), 86–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

