Activation of interferon response through toll-like receptor 3 impacts viral pathogenesis and pulmonary toll-like receptor expression during respiratory syncytial virus and influenza infections in the cotton rat Sigmodon hispidus model
- PMID: 20038196
- PMCID: PMC2882628
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2009.0025
Activation of interferon response through toll-like receptor 3 impacts viral pathogenesis and pulmonary toll-like receptor expression during respiratory syncytial virus and influenza infections in the cotton rat Sigmodon hispidus model
Abstract
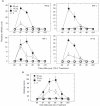
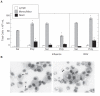
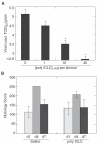
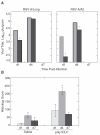
Interferon (IFN) therapy in humans often causes flu-like symptoms by an unknown mechanism. Poly ICLC is a synthetic dsRNA and a Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) agonist with a strong IFN-inducing ability. In this work, we analyzed the effect of poly ICLC on pulmonary responses to influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections in the cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) model. Viral replication, pulmonary inflammation, and expression of IFN, TLR, and chemokines were monitored and compared. Antiviral effect of poly ICLC against influenza virus and RSV was best achieved at high poly ICLC concentrations that, in the absence of virus infection, induced a strong IFN response. The antiviral doses of poly ICLC, however, also increased lung inflammation, an unexpected finding because of the reported poly ICLC safety in BALB/c mice. Similarly, in contrast to murine model, pathology of RSV infection was increased in cotton rats treated with poly ICLC. Augmented lung inflammation was accompanied by an earlier induction of IFN and TLR responses and a stronger chemokine expression. Overall, these findings indicate significant association between antiviral IFN action and pulmonary inflammation and highlight important animal model-specific variations in the potential of IFN to cause pathology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway for protection against influenza virus infection.Vaccine. 2009 May 26;27(25-26):3481-3. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.048. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 19200852 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and regulation of alpha interferon in respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus experimental infections.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10190-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10190-10199.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051812 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and Chronic Airway Disease After Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Cotton Rats (Sigmodon hispidus).Comp Med. 2015 Aug;65(4):315-26. Comp Med. 2015. PMID: 26310461 Free PMC article.
-
Cotton rat model for testing vaccines and antivirals against respiratory syncytial virus.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2018 Jan-Dec;26:2040206618770518. doi: 10.1177/2040206618770518. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29768937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly-ICLC, a multi-functional immune modulator for treating cancer.Semin Immunol. 2020 Jun;49:101414. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2020.101414. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Semin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33011064 Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor 3 pathway restricts Marek's disease virus infection.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 7;8(41):70847-70853. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20003. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050325 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Susceptibility of Neonates to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Problem of Innate Immunity?J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:8734504. doi: 10.1155/2017/8734504. Epub 2017 Nov 9. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 29250560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems biology unravels interferon responses to respiratory virus infections.World J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 26;5(1):12-25. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i1.12. World J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24600511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal immunization with a single dose of the fusion protein formulated with a combination adjuvant induces long-term protective immunity against respiratory syncytial virus.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017 Dec 2;13(12):2894-2901. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1349584. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28825870 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Toll-like receptor 3 impairs the dengue virus serotype 2 replication through induction of IFN-β in cultured hepatoma cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023346. Epub 2011 Aug 4. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Blanco JC, Pletneva L, Boukhvalova M, Richardson JY, Harris KA, Prince GA. The cotton rat: an underutilized animal model for human infectious diseases can now be exploited using specific reagents to cytokines, chemokines, and interferons. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004;24:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Blanco JC, Richardson JY, Darnell ME, Rowzee A, Pletneva L, Porter DD, Prince GA. Cytokine and chemokine gene expression after primary and secondary respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:1780–1785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

