Inactivation of the KcsA potassium channel explored with heterotetramers
- PMID: 20038524
- PMCID: PMC2806417
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200910305
Inactivation of the KcsA potassium channel explored with heterotetramers
Abstract
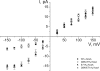
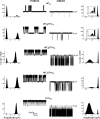
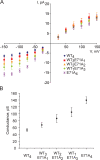
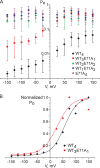
The tetrameric prokaryotic potassium channel KcsA is activated by protons acting on the intracellular aspect of the protein and inactivated through conformational changes in the selectivity filter. Inactivation is modulated by a network of interactions within each protomer between the pore helix and residues at the external entrance of the channel. Inactivation is suppressed by the E71A mutation, which perturbs the stability of this network. Here, cell-free protein synthesis followed by protein purification by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was used to produce heterotetramers of KcsA that contain different combinations of wild-type and E71A subunits. Single-channel recordings from these heterotetramers reveal how the network of interactions in individual protomers affects ionic conduction and channel inactivation, suggesting that the latter is a cooperative process.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mechanism for selectivity-inactivation coupling in KcsA potassium channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 29;108(13):5272-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014186108. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21402935 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic state of the cytoplasmic domain influences inactivation at the selectivity filter of the KcsA potassium channel.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019 Jan;1861(1):220-227. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 30053405
-
The potassium channel KcsA and its interaction with the lipid bilayer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003 Aug;60(8):1581-90. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3172-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 14513833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium permeability and sensitivity induced by mutations in the selectivity filter of the KcsA channel towards Kir channels.Biochimie. 2010 Mar;92(3):232-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2009.11.007. Epub 2009 Dec 3. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 19962419
-
Diverse gating in K+ channels: differential role of the pore-helix glutamate in stabilizing the channel pore.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Sep 16;413(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.062. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21872570 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated parallel recordings of topologically identified single ion channels.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1995. doi: 10.1038/srep01995. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23771282 Free PMC article.
-
A multipoint hydrogen-bond network underlying KcsA C-type inactivation.Biophys J. 2011 May 18;100(10):2387-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.01.073. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21575572 Free PMC article.
-
Anionic Phospholipids Shift the Conformational Equilibrium of the Selectivity Filter in the KcsA Channel to the Conductive Conformation: Predicted Consequences on Inactivation.Biomedicines. 2023 May 5;11(5):1376. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051376. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239046 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution and functional characterization of ion channels from nanodiscs in lipid bilayers.J Gen Physiol. 2018 Apr 2;150(4):637-646. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711904. Epub 2018 Feb 27. J Gen Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29487088 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of membrane bilayer thickness on KcsA channel activity.Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):424-439. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1676367. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 31608774 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

