The activation mechanism of alpha1beta2gamma2S and alpha3beta3gamma2S GABAA receptors
- PMID: 20038526
- PMCID: PMC2806416
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200910317
The activation mechanism of alpha1beta2gamma2S and alpha3beta3gamma2S GABAA receptors
Abstract
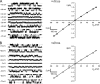
The alpha1beta2gamma2 and alpha3beta3gamma2 are two isoforms of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor that are widely distributed in the brain. Both are found at synapses, for example in the thalamus, where they mediate distinctly different inhibitory postsynaptic current profiles, particularly with respect to decay time. The two isoforms were expressed in HEK293 cells, and single-channel activity was recorded from outside-out patches. The kinetic characteristics of both isoforms were investigated by analyzing single-channel currents over a wide range of GABA concentrations. Alpha1beta2gamma2 channels exhibited briefer active periods than alpha3beta3gamma2 channels over the entire range of agonist concentrations and had lower intraburst open probabilities at subsaturating concentrations. Activation mechanisms were constructed by fitting postulated schemes to data recorded at saturating and subsaturating GABA concentrations simultaneously. Reaction mechanisms were ranked according to log-likelihood values and how accurately they simulated ensemble currents. The highest ranked mechanism for both channels consisted of two sequential binding steps, followed by three conducting and three nonconducting configurations. The equilibrium dissociation constant for GABA at alpha3beta3gamma2 channels was approximately 2.6 microM compared with approximately 19 microM for alpha1beta2gamma2 channels, suggesting that GABA binds to the alpha3beta3gamma2 channels with higher affinity. A notable feature of the mechanism was that two consecutive doubly liganded shut states preceded all three open configurations. The lifetime of the third shut state was briefer for the alpha3beta3gamma2 channels. The longer active periods, higher affinity, and preference for conducting states are consistent with the slower decay of inhibitory currents at synapses that contain alpha3beta3gamma2 channels. The reaction mechanism we describe here may also be appropriate for the analysis of other types of GABAA receptors and provides a framework for rational investigation of the kinetic effects of a variety of therapeutic agents that activate or modulate GABAA receptors and hence influence synaptic and extrasynaptic inhibition in the central nervous system.
Figures


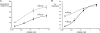



Similar articles
-
Agonist-dependent single channel current and gating in alpha4beta2delta and alpha1beta2gamma2S GABAA receptors.J Gen Physiol. 2008 Feb;131(2):163-81. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709871. J Gen Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18227274 Free PMC article.
-
Desensitization and binding properties determine distinct alpha1beta2gamma2 and alpha3beta2gamma2 GABA(A) receptor-channel kinetic behavior.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 May;25(9):2726-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05530.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17561840 Free PMC article.
-
Modes and models of GABA(A) receptor gating.J Physiol. 2006 Apr 1;572(Pt 1):183-200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.099093. Epub 2006 Feb 2. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16455693 Free PMC article.
-
Loop G in the GABAA receptor α1 subunit influences gating efficacy.J Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;595(5):1725-1741. doi: 10.1113/JP273752. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27981574 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutically leveraging GABAA receptors in cancer.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Oct;246(19):2128-2135. doi: 10.1177/15353702211032549. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34649481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Inhibitory Signaling at the Receptor and Cellular Level; Advances in Our Understanding of GABAergic Neurotransmission and the Mechanisms by Which It Is Disrupted in Epilepsy.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 Jun 15;14:914374. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2022.914374. eCollection 2022. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35874848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABAA receptor α and γ subunits shape synaptic currents via different mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):5399-411. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514695. Epub 2014 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24425869 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous expression of GABA receptor-like subunits LCCH3 and GRD reveals functional diversity of GABA receptors in the honeybee Apis mellifera.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;177(17):3924-3940. doi: 10.1111/bph.15135. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32436264 Free PMC article.
-
A single main-chain hydrogen bond required to keep GABAA receptors closed.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 3;16(1):6107. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61447-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40603861 Free PMC article.
-
Maximum likelihood estimation of biophysical parameters of synaptic receptors from macroscopic currents.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Oct 2;8:303. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00303. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25324721 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

