Lysine 63-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 at lysine 158 is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha- and interleukin-1beta-induced IKK/NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation
- PMID: 20038579
- PMCID: PMC2820763
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076976
Lysine 63-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 at lysine 158 is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha- and interleukin-1beta-induced IKK/NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation
Abstract
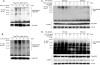
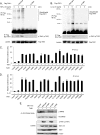
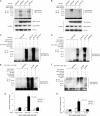
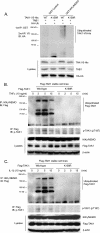
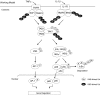
Transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) plays an essential role in the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha)- and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta)-induced IkappaB kinase (IKK)/nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/activator protein 1 (AP-1) activation. Here we report that TNFalpha and IL-1beta induce Lys(63)-linked TAK1 polyubiquitination at the Lys(158) residue within the kinase domain. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors 2 and 6 (TRAF2 and -6) act as the ubiquitin E3 ligases to mediate Lys(63)-linked TAK1 polyubiquitination at the Lys(158) residue in vivo and in vitro. Lys(63)-linked TAK1 polyubiquitination at the Lys(158) residue is required for TAK1-mediated IKK complex recruitment. Reconstitution of TAK1-deficient mouse embryo fibroblast cells with TAK1 wild type or a TAK1 mutant containing a K158R mutation revealed the importance of this site in TNFalpha and IL-1beta-mediated IKK/NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation as well as IL-6 gene expression. Our findings demonstrate that Lys(63)-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 at Lys(158) is essential for its own kinase activation and its ability to mediate its downstream signal transduction pathways in response to TNFalpha and IL-1beta stimulation.
Figures



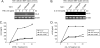
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

