Map4k4 negatively regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma protein translation by suppressing the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in cultured adipocytes
- PMID: 20038583
- PMCID: PMC2825455
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068502
Map4k4 negatively regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma protein translation by suppressing the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in cultured adipocytes
Abstract
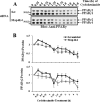
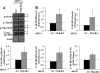
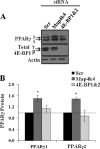
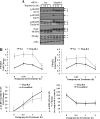
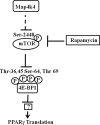
The receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) is considered a master regulator of adipocyte differentiation and promotes glucose and lipid metabolism in mature adipocytes. We recently identified the yeast Sterile 20 (Ste20) protein kinase ortholog, Map4k4, in an RNA interference-based screen as an inhibitor of PPARgamma expression in cultured adipocytes. Here, we show that RNA interference-mediated silencing of Map4k4 elevates the levels of both PPARgamma1 and PPARgamma2 proteins in 3T3-L1 adipocytes without affecting PPARgamma mRNA levels, suggesting that Map4k4 regulates PPARgamma at a post-transcriptional step. PPARgamma degradation rates are remarkably rapid as measured in the presence of cycloheximide (t(1/2) = 2 h), but silencing Map4k4 had no effect on PPARgamma degradation. However, depletion of Map4k4 significantly enhances [(35)S]methionine/cysteine incorporation into proteins, suggesting that Map4k4 signaling decreases protein translation. We show a function of Map4k4 is to inhibit rapamycin-sensitive mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity, decreasing 4E-BP1 phosphorylation. In addition, our results show mTOR and 4E-BP1 are required for the increased PPARgamma protein expression upon Map4k4 knockdown. Consistent with this concept, adenovirus-mediated expression of Map4k4 decreased PPARgamma protein levels and mTOR phosphorylation. These data show that Map4k4 negatively regulates PPARgamma post-transcriptionally, by attenuating mTOR signaling and a 4E-BP1-dependent mechanism.
Figures
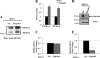

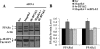
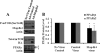
Similar articles
-
An RNA interference-based screen identifies MAP4K4/NIK as a negative regulator of PPARgamma, adipogenesis, and insulin-responsive hexose transport.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 14;103(7):2087-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507660103. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16461467 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of insulin signaling and adipogenesis by rapamycin: effect on phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase vs eIF4E-BP1.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004 Feb;28(2):191-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802554. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004. PMID: 14970836
-
Map4k4 suppresses Srebp-1 and adipocyte lipogenesis independent of JNK signaling.J Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;54(10):2697-707. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M038802. Epub 2013 Aug 7. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23924694 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi screens reveal novel metabolic regulators: RIP140, MAP4k4 and the lipid droplet associated fat specific protein (FSP) 27.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2008 Jan;192(1):103-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01786.x. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2008. PMID: 18171433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic modulation of JAK-STAT, mTOR, and PPAR-γ signaling in neurological dysfunctions.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Feb;101(1-2):9-49. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02272-6. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 36478124 Review.
Cited by
-
Map4k4 Signaling Nodes in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul;27(7):484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 May 6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27160798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radix Astragali Improves Dysregulated Triglyceride Metabolism and Attenuates Macrophage Infiltration in Adipose Tissue in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Male Rats through Activating mTORC1-PPAR γ Signaling Pathway.PPAR Res. 2014;2014:189085. doi: 10.1155/2014/189085. Epub 2014 Apr 8. PPAR Res. 2014. PMID: 24817881 Free PMC article.
-
RBM4a-SRSF3-MAP4K4 Splicing Cascade Constitutes a Molecular Mechanism for Regulating Brown Adipogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 6;19(9):2646. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092646. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30200638 Free PMC article.
-
Latexin deficiency attenuates adipocyte differentiation and protects mice against obesity and metabolic disorders induced by high-fat diet.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 24;13(2):175. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04636-9. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35210404 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammatory kinase MAP4K4 promotes reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus and enhances the invasiveness of infected endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(11):e1003737. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003737. Epub 2013 Nov 7. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24244164 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

