The Streptococcus mutans IrvR repressor is a CI-like regulator that functions through autocleavage and Clp-dependent proteolysis
- PMID: 20038591
- PMCID: PMC2832535
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01261-09
The Streptococcus mutans IrvR repressor is a CI-like regulator that functions through autocleavage and Clp-dependent proteolysis
Abstract
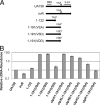
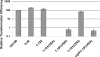
Previous work has shown that irvR is required for the proper regulation of genetic competence and dextran-dependent aggregation due to its ability to repress the transcription regulator irvA. In this study, we determined the mechanism used to relieve the repression of irvA. We demonstrate that IrvR is a "LexA-like" protein with four conserved amino acid residues likely required for IrvR autocleavage activity. Furthermore, recombinant IrvR protein purified from Escherichia coli was competent to undergo autocleavage in vitro. Using several truncated IrvR constructs, we show that the amino acids adjacent to the autocleavage site are essential for relieving irvA repression and engaging the irvA-dependent regulatory pathway primarily through the ClpXP and ClpCP proteases. By extending the IrvR C terminus with an epitope derived from the autocleavage site, we were also able to create a constitutive Clp-dependent degradation of the full-length IrvR protein. This suggests that the derepression of irvA occurs through a two-step mechanism involving the initial autocleavage of IrvR and exposure of a proteolytic degradation sequence followed by Clp-dependent degradation of the IrvR DNA binding domain. Thus, irvA derepression is highly analogous to the genetic switch mechanism used to regulate lysogeny in bacteriophages.
Figures

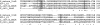



Similar articles
-
Characterization of irvR, a novel regulator of the irvA-dependent pathway required for genetic competence and dextran-dependent aggregation in Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2008 Nov;190(21):7268-74. doi: 10.1128/JB.00967-08. Epub 2008 Aug 29. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18757533 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Streptococcus mutans irvA gene in GbpC-independent, dextran-dependent aggregation and biofilm formation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Nov;75(22):7037-43. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01015-09. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19783751 Free PMC article.
-
IrvA-dependent and IrvA-independent pathways for mutacin gene regulation in Streptococcus mutans.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Aug;261(2):231-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00351.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16907725
-
MecA: A Multifunctional ClpP-Dependent and Independent Regulator in Gram-Positive Bacteria.Mol Microbiol. 2025 May;123(5):433-438. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15356. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Mol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40070161 Review.
-
Comparative genomics and functional roles of the ATP-dependent proteases Lon and Clp during cytosolic protein degradation.Res Microbiol. 2004 Nov;155(9):710-9. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2004.06.003. Res Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15501647 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA regulators of host immunity and pathogen adaptive responses in the oral cavity.Microbes Infect. 2015 Jul;17(7):493-504. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Microbes Infect. 2015. PMID: 25790757 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription regulator BrsR serves as a network hub of natural competence protein-protein interactions in Streptococcus mutans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 28;118(39):e2106048118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106048118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34544866 Free PMC article.
-
The Streptococcus mutans irvA gene encodes a trans-acting riboregulatory mRNA.Mol Cell. 2015 Jan 8;57(1):179-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.003. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25574948 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of FtsH Essentiality in Streptococcus mutans via Genetic Suppression.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 27;12:659220. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.659220. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33986772 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-Dependent Recognition of a Unique Degradation Motif by ClpXP in Streptococcus mutans.mSphere. 2016 Dec 7;1(6):e00287-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00287-16. eCollection 2016 Nov-Dec. mSphere. 2016. PMID: 27981232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banas, J. A. 2004. Virulence properties of Streptococcus mutans. Front. Biosci. 9:1267-1277. - PubMed
-
- Barsamian-Wunsch, P., J. H. Park, M. R. Watson, N. Tinanoff, and G. E. Minah. 2004. Microbiological screening for cariogenic bacteria in children 9 to 36 months of age. Pediatr. Dent. 26:231-239. - PubMed
-
- Bowden, G. H. 1990. Microbiology of root surface caries in humans. J. Dent. Res. 69:1205-1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

