Cellular IAPs inhibit a cryptic CD95-induced cell death by limiting RIP1 kinase recruitment
- PMID: 20038679
- PMCID: PMC2806279
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904158
Cellular IAPs inhibit a cryptic CD95-induced cell death by limiting RIP1 kinase recruitment
Abstract
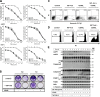
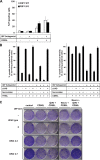
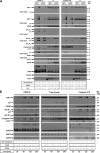
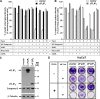
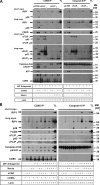
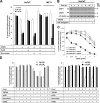
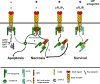
A role for cellular inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs [cIAPs]) in preventing CD95 death has been suspected but not previously explained mechanistically. In this study, we find that the loss of cIAPs leads to a dramatic sensitization to CD95 ligand (CD95L) killing. Surprisingly, this form of cell death can only be blocked by a combination of RIP1 (receptor-interacting protein 1) kinase and caspase inhibitors. Consistently, we detect a large increase in RIP1 levels in the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) and in a secondary cytoplasmic complex (complex II) in the presence of IAP antagonists and loss of RIP1-protected cells from CD95L/IAP antagonist-induced death. Cells resistant to CD95L/IAP antagonist treatment could be sensitized by short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (cFLIP). However, only cFLIP(L) and not cFLIP(S) interfered with RIP1 recruitment to the DISC and complex II and protected cells from death. These results demonstrate a fundamental role for RIP1 in CD95 signaling and provide support for a physiological role of caspase-independent death receptor-mediated cell death.
Figures


References
-
- Bertrand M.J., Milutinovic S., Dickson K.M., Ho W.C., Boudreault A., Durkin J., Gillard J.W., Jaquith J.B., Morris S.J., Barker P.A. 2008. cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. 30:689–700 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.014 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blankenship J.W., Varfolomeev E., Goncharov T., Fedorova A.V., Kirkpatrick D.S., Izrael-Tomasevic A., Phu L., Arnott D., Aghajan M., Zobel K., et al. 2009. Ubiquitin binding modulates IAP antagonist-stimulated proteasomal degradation of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2(1). Biochem. J. 417:149–160 10.1042/BJ20081885 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

