Genome-wide screening and identification of factors affecting the biosynthesis of prodigiosin by Hahella chejuensis, using Escherichia coli as a surrogate host
- PMID: 20038694
- PMCID: PMC2832371
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01468-09
Genome-wide screening and identification of factors affecting the biosynthesis of prodigiosin by Hahella chejuensis, using Escherichia coli as a surrogate host
Abstract
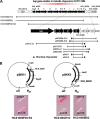
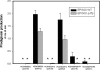
A marine bacterium, Hahella chejuensis, recently has attracted attention due to its lytic activity against a red-tide dinoflagellate. The algicidal function originates from its red pigment, prodigiosin, which also exhibits immunosuppressive or anticancer activity. Genome sequencing and functional analysis revealed a gene set contained in the hap gene cluster that is responsible for the biosynthesis of prodigiosin. To screen for the factors affecting the prodigiosin biosynthesis, we constructed a plasmid library of the H. chejuensis genomic DNA, introduced it into Escherichia coli strains harboring the hap cluster, and observed changes in production of the red pigment. Among the screened clones, hapXY genes whose products constitute a two-component signal transduction system were elucidated as positive regulators of the pigment production. In addition, an Hfq-dependent, noncoding region located at one end of the hap cluster was confirmed to play roles in regulation. Identification of factors involved in the regulation of prodigiosin biosynthesis should help in understanding how the prodigiosin-biosynthetic pathway is organized and controlled and also aid in modulating the overexpression of prodigiosin in a heterologous host, such as E. coli, or in the natural producer, H. chejuensis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Red to red - the marine bacterium Hahella chejuensis and its product prodigiosin for mitigation of harmful algal blooms.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 Oct;18(10):1621-9. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18955809 Review.
-
Genomic blueprint of Hahella chejuensis, a marine microbe producing an algicidal agent.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Dec 13;33(22):7066-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki1016. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16352867 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant selection of Hahella chejuensis KCTC 2396 and statistical optimization of medium components for prodigiosin yield-up.J Microbiol. 2008 Apr;46(2):183-8. doi: 10.1007/s12275-008-0037-y. Epub 2008 Jun 11. J Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18545968
-
Discovery of New Secondary Metabolites from Marine Bacteria Hahella Based on an Omics Strategy.Mar Drugs. 2022 Apr 18;20(4):269. doi: 10.3390/md20040269. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447942 Free PMC article.
-
The biosynthesis and regulation of bacterial prodiginines.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006 Dec;4(12):887-99. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1531. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17109029 Review.
Cited by
-
Biotechnological Activities and Applications of Bacterial Pigments Violacein and Prodigiosin.J Biol Eng. 2021 Mar 11;15(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13036-021-00262-9. J Biol Eng. 2021. PMID: 33706806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying Algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 21;19(13):7556. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137556. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35805215 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an algicidal compound from Brevibacterium sp. BS01 and its effect on a harmful algal bloom-causing species, Alexandrium tamarense.Front Microbiol. 2015 Nov 5;6:1235. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01235. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26594205 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genome and transcriptome analysis of diatom, Skeletonema costatum, reveals evolution of genes for harmful algal bloom.BMC Genomics. 2018 Oct 22;19(1):765. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5144-5. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30348078 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of the algicidal bacterium Kordia algicida with diatoms: regulated protease excretion for specific algal lysis.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021032. Epub 2011 Jun 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravind, L., and C. P. Ponting. 1999. The cytoplasmic helical linker domain of receptor histidine kinase and methyl-accepting proteins is common to many prokaryotic signalling proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 176:111-116. - PubMed
-
- Doucette, G. J. 1995. Interactions between bacteria and harmful algae: a review. Nat. Toxins 3:65-74. - PubMed
-
- Fineran, P. C., H. Slater, L. Everson, K. Hughes, and G. P. Salmond. 2005. Biosynthesis of tripyrrole and β-lactam secondary metabolites in Serratia: integration of quorum sensing with multiple new regulatory components in the control of prodigiosin and carbapenem antibiotic production. Mol. Microbiol. 56:1495-1517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

