Biogenic silver for disinfection of water contaminated with viruses
- PMID: 20038697
- PMCID: PMC2820954
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02433-09
Biogenic silver for disinfection of water contaminated with viruses
Abstract
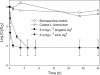
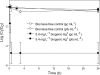
The presence of enteric viruses in drinking water is a potential health risk. Growing interest has arisen in nanometals for water disinfection, in particular the use of silver-based nanotechnology. In this study, Lactobacillus fermentum served as a reducing agent and bacterial carrier matrix for zerovalent silver nanoparticles, referred to as biogenic Ag(0). The antiviral action of biogenic Ag(0) was examined in water spiked with an Enterobacter aerogenes-infecting bacteriophage (UZ1). Addition of 5.4 mg liter(-1) biogenic Ag(0) caused a 4.0-log decrease of the phage after 1 h, whereas the use of chemically produced silver nanoparticles (nAg(0)) showed no inactivation within the same time frame. A control experiment with 5.4 mg liter(-1) ionic Ag+ resulted in a similar inactivation after 5 h only. The antiviral properties of biogenic Ag(0) were also demonstrated on the murine norovirus 1 (MNV-1), a model organism for human noroviruses. Biogenic Ag(0) was applied to an electropositive cartridge filter (NanoCeram) to evaluate its capacity for continuous disinfection. Addition of 31.25 mg biogenic Ag(0) m(-2) on the filter (135 mg biogenic Ag(0) kg(-1) filter medium) caused a 3.8-log decline of the virus. In contrast, only a 1.5-log decrease could be obtained with the original filter. This is the first report to demonstrate the antiviral efficacy of extracellular biogenic Ag(0) and its promising opportunities for continuous water disinfection.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, M. H. 1959. Bacteriophages. Interscience, New York, NY.
-
- Ahmad, A., P. Mukherjee, S. Senapati, D. Mandal, M. I. Khan, R. Kumar, and M. Sastry. 2003. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 28:313-318.
-
- Benn, T. M., and P. Westerhoff. 2008. Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42:4133-4139. - PubMed
-
- Birla, S. S., V. V. Tiwari, A. K. Gade, A. P. Ingle, A. P. Yadav, and M. K. Rai. 2009. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles by Phoma glomerata and its combined effect against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 48:173-179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

