Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates murine and human cell differentiation through STAT3/p63/Jagged/Notch cascade
- PMID: 20038814
- PMCID: PMC2798675
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI37964
Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates murine and human cell differentiation through STAT3/p63/Jagged/Notch cascade
Abstract
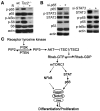
The receptor tyrosine kinase/PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (RTK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR) pathway is frequently altered in cancer, but the underlying mechanism leading to tumorigenesis by activated mTOR remains less clear. Here we show that mTOR is a positive regulator of Notch signaling in mouse and human cells, acting through induction of the STAT3/p63/Jagged signaling cascade. Furthermore, in response to differential cues from mTOR, we found that Notch served as a molecular switch to shift the balance between cell proliferation and differentiation. We determined that hyperactive mTOR signaling impaired cell differentiation of murine embryonic fibroblasts via potentiation of Notch signaling. Elevated mTOR signaling strongly correlated with enhanced Notch signaling in poorly differentiated but not in well-differentiated human breast cancers. Both human lung lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) and mouse kidney tumors with hyperactive mTOR due to tumor suppressor TSC1 or TSC2 deficiency exhibited enhanced STAT3/p63/Notch signaling. Furthermore, tumorigenic potential of cells with uncontrolled mTOR signaling was suppressed by Notch inhibition. Our data therefore suggest that perturbation of cell differentiation by augmented Notch signaling might be responsible for the underdifferentiated phenotype displayed by certain tumors with an aberrantly activated RTK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Additionally, the STAT3/p63/Notch axis may be a useful target for the treatment of cancers exhibiting hyperactive mTOR signaling.
Figures






Comment in
-
New roles for Notch in tuberous sclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jan;120(1):84-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI41897. Epub 2009 Dec 28. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20038806 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of Notch-1 and Jagged-1 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis via inactivation of Akt, mTOR, and NF-kappaB signaling pathways.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Mar 1;109(4):726-36. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22451. J Cell Biochem. 2010. Retraction in: J Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;117(8):1960. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25585. PMID: 20052673 Retracted.
-
Yes-associated protein up-regulates Jagged-1 and activates the Notch pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2013 Jun;144(7):1530-1542.e12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.009. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23419361 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenergic signaling promotes angiogenesis through endothelial cell-tumor cell crosstalk.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014 Oct;21(5):783-95. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0236. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25179535
-
Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review.
-
Notch signaling regulates tumor angiogenesis by diverse mechanisms.Oncogene. 2008 Sep 1;27(38):5132-7. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.227. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18758482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mTORC1 regulates PTHrP to coordinate chondrocyte growth, proliferation and differentiation.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 4;7:11151. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11151. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27039827 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression Profile of microRNAs and Tight Junction in the Lung Tissues of Rat With Mitomycin-C-Induced Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 16;9:746888. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.746888. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35252374 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin up-regulation of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 is critical for aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 8;108(10):4129-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014769108. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21325052 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition on T helper type 17 and regulatory T cell differentiation in vitro and in vivo in kidney transplant recipients.Immunology. 2015 Jan;144(1):68-78. doi: 10.1111/imm.12351. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 24974886 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hyperactivated mTORC1 downregulation of FOXO3a/PDGFRα/AKT cascade restrains tuberous sclerosis complex-associated tumor development.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 4;8(33):54858-54872. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18963. eCollection 2017 Aug 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28903387 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

