The molecular pathogenesis of head and neck cancer
- PMID: 20038820
- PMCID: PMC3138532
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.9.1.10905
The molecular pathogenesis of head and neck cancer
Abstract
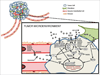
Head and neck cancer arises from a series of molecular alterations progressive from dysplasia to carcinoma in situ, and finally invasive carcinoma. Risk factors associated with head and neck cancer include tobacco, alcohol and viral infection. There are genetic alterations in pre-cancerous cells that contribute to transformation. The accumulation of these alterations facilitates tumor development. Additionally, the tumor microenvironment enables tumor progression. The cooperative effect of molecular alterations in the tumor cells and compensatory microenvironment changes enable tumors to invade and metastasize. This review focuses on the genes and molecules altered during the progression of head and neck cancer with an emphasis on the genetic, molecular and phenotypic changes during the pathogenesis of head and neck cancer. Therapeutic strategies that target key changes in the tumor cells and/or stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Curado M, Hashibe M. Recent changes in the epidemiology. Curr Opin Oncol. 2009;21:194–200. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer Statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Gillison ML. Current topics in the epidemiology of oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. Head Neck. 2007;29:779–92. - PubMed
-
- Hashibe M, Brennan P, Benhamou S, Castellsague X, Chen C, Curado MP, et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:777–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
