Parenteral fish oil as monotherapy prevents essential fatty acid deficiency in parenteral nutrition-dependent patients
- PMID: 20038849
- PMCID: PMC3365554
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181bbf51e
Parenteral fish oil as monotherapy prevents essential fatty acid deficiency in parenteral nutrition-dependent patients
Abstract
Objective: The use of fish oil-based emulsions as the sole source of fat for patients receiving parenteral nutrition (PN) has raised concerns for the development of essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD), hindering its adoption into clinical practice. The purpose of the present study was to examine fatty acid profiles of patients receiving no enteral energy, while completely dependent on PN and an intravenous fish oil-based lipid emulsion, for onset of EFAD and maintenance of growth.
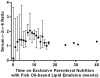
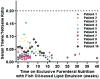
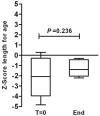
Patients and methods: Prospectively collected data from 10 patients were reviewed for evidence of EFAD, defined as a triene:tetraene ratio >0.2. Gestational age-adjusted z scores for length, growth, and head circumference at baseline were compared with the corresponding z scores at time of censoring. All of the patients received PN with a fish oil-based lipid emulsion at 1 g . kg . day as the sole source of fat energy for at least 1 month. The fish oil monotherapy was used under a compassionate use protocol.
Results: Median gestational age at the time of birth was 35 weeks, and median age at the start of treatment was 3.5 months. After a median time of 3.8 months on exclusive PN and fish oil-based lipid emulsion, none of the patients developed biochemical or clinical evidence of EFAD. z scores were not statistically different, indicating no growth impairment. Median direct bilirubin levels improved in 9 patients from 6.8 to 0.9 mg/dL (P = 0.009).
Conclusions: : When dosed appropriately, fish oil-based lipid emulsions contain sufficient amounts of essential fatty acids to prevent EFAD and sustain growth in patients who are completely dependent on PN.
Figures




References
-
- MacFie J. The development of fat emulsions. Nutrition. 1999;15:641, 643–5. - PubMed
-
- Wretlind A. Development of fat emulsions. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1981;5:230–5. - PubMed
-
- Clayton PT, Bowron A, Mills KA, et al. Phytosterolemia in children with parenteral nutrition-associated cholestatic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:1806–13. - PubMed
-
- Chen WJ, Yeh SL, Huang PC. Effects of fat emulsions with different fatty acid composition on plasma and hepatic lipids in rats receiving total parenteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. 1996;15:24–8. - PubMed
-
- De Meijer VE, Gura KM, Le HD, et al. Fish oil-based lipid emulsions prevent and reverse parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: the Boston experience. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2009 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

