C-Peptide: the missing link in diabetic nephropathy?
- PMID: 20039009
- PMCID: PMC2827272
- DOI: 10.1900/RDS.2009.6.203
C-Peptide: the missing link in diabetic nephropathy?
Abstract
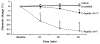
Proinsulin C-peptide has been found to exert beneficial effects in many tissues affected by diabetic microvascular complications, including the kidneys. Glomerular hyperfiltration and microalbuminuria are early markers of diabetic nephropathy. C-peptide at physiological concentrations effectively reduces diabetes-induced glomerular hyperfiltration via constriction of the afferent arteriole, dilation of the efferent arteriole, and inhibition of tubular reabsorption in experimental models of type 1 diabetes. The glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial matrix expansion seen in early diabetes can be reduced or prevented by C-peptide administration, possibly via interference with TGF-beta1 and TNFalpha signaling. Several of C-peptide's reno-protective effects have been confirmed in human studies; reduced glomerular hyperfiltration and diminished urinary albumin excretion have been documented in type 1 diabetes patients receiving replacement doses of C-peptide for periods of up to 3 months. In this review, we critically summarize the current state of knowledge regarding C-peptide's renal effects, and discuss possible mechanisms of its beneficial effects in diabetic nephropathy.
Figures
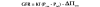

References
-
- O'Bryan GT, Hostetter TH. The renal hemodynamic basis of diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 1997;17(2):93–100. - PubMed
-
- Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Sutherland DE, Goetz FC, Mauer M. Reversal of lesions of diabetic nephropathy after pancreas transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Fiorina P, Folli F, Zerbini G, Maffi P, Gremizzi C, Di Carlo V, Socci C, Bertuzzi F, Kashgarian M, Secchi A. Islet transplantation is associated with improvement of renal function among uremic patients with type I diabetes mellitus and kidney transplants. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2150–2158. - PubMed
-
- Johansson BL, Borg K, Fernqvist-Forbes E, Kernell A, Odergren T, Wahren J. Beneficial effects of C-peptide on incipient nephropathy and neuropathy in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2000;17:181–189. - PubMed
-
- Johansson BL, Kernell A, Sjoberg S, Wahren J. Influence of combined C-peptide and insulin administration on renal function and metabolic control in diabetes type 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993;77:976–981. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
