Sequential abnormalities in type 1 diabetic encephalopathy and the effects of C-Peptide
- PMID: 20039010
- PMCID: PMC2827273
- DOI: 10.1900/RDS.2009.6.211
Sequential abnormalities in type 1 diabetic encephalopathy and the effects of C-Peptide
Abstract
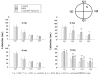
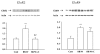
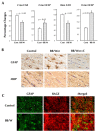
Diabetic encephalopathy is a recently recognized complication in type 1 diabetes. In this review, we summarize a series of experimental results obtained longitudinally in the spontaneously type 1 diabetic BB/Wor-rat, and bringing out the beneficial effects of C-peptide replacement. It is increasingly clear that lack of insulin and C-peptide, and perturbations of their signaling cascades in type 1 diabetes are detrimental to the regulation of neurotrophic factors and their receptors. Other consequences of such deficits and perturbations are innate inflammatory responses with effects on synaptogenesis, neurite degeneration, and early behavioral abnormalities. Replacement of C-peptide, which does not effect hyperglycemia, has beneficial effects on a variety of pro-apoptotic stressors, oxidative stressors, and finally on apoptosis. Eventually, this cascade of events leads to neuronal loss and decreased densities of white matter myelinating cells, with more profound deficits in behavioral and cognitive function. Such changes are likely to underlie gray and white matter atrophy in type 1 diabetes, and are significantly prevented by full C-peptide replacement. Present data demonstrate that C-peptide replacement has beneficial effects on numerous sequential and partly interrelated pathogenetic mechanisms, resulting in prevention of neuronal and oligodendroglial cell loss, with significant prevention of neurobehavioral and cognitive functions.
Figures

References
-
- Sima AA, Kamiya H, Li ZG. Insulin, C-peptide hyperglycemia and central nervous system complications in diabetes. Europ J Pharmacol. 2004;490:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Biessels GJ, Deary TJ, Ryan CM. Cognition and diabetes: a lifespan perspective. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:184–190. - PubMed
-
- Biessels GJ. Diabetic encephalopathy. In: Veves A, Malik RA, editors. Diabetic Neuropathy - Clinical Management. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: 2007. pp. 187–205.
-
- Sima AA. Pathobiology of diabetic encephalopathy. In: Biessels GJ, Luchsinger JA, editors. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: 2009. pp. 405–427.
-
- Zhang W, Sima AA. The role glucose, cholesterol and insulin have in amyloidogenesis in human neuroblastoma cells. Toronto, Canada. Proc XIX in Meeting of Neurodiab; 2009. p. 21. Abstract.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
