The enhancement of antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity of HDAC inhibitors by curcumin is mediated by Hsp90 inhibition
- PMID: 20039095
- PMCID: PMC11115870
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0233-x
The enhancement of antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity of HDAC inhibitors by curcumin is mediated by Hsp90 inhibition
Abstract
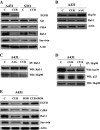
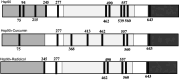
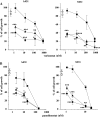
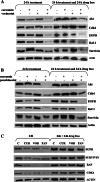
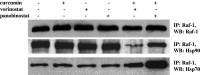
Curcumin, a natural polyphenol, has been described to exhibit effects on signaling pathways, leading to induction of apoptosis. In this study, we observed that curcumin inhibited Hsp90 activity causing depletion of client proteins implicated in survival pathways. Based on this observation, this study was designed to investigate the cellular effects of curcumin combination with the pan-HDAC inhibitors, vorinostat and panobinostat, which induce hyperacetylation of Hsp90, resulting in inhibition of its chaperone function. The results showed that, at subtoxic concentrations, curcumin markedly sensitized tumor cells to vorinostat- and panobinostat-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. The sensitization was associated with persistent depletion of Hsp90 client proteins (EGFR, Raf-1, Akt, and survivin). In conclusion, our findings document a novel mechanism of action of curcumin and support the therapeutic potential of curcumin/HDAC inhibitors combination, because the synergistic interaction was observed at pharmacologically achievable concentrations, which were ineffective when each drug was used alone.
Figures


References
-
- Kawamori T, Lubet R, Steele VE, Kelloff GJ, Kaskey RB, Rao CV, Reddy BS. Chemopreventive effect of curcumin, a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory agent, during the promotion/progression stages of colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1999;59:597–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

