Lack of effect of a single injection of human C-reactive protein on murine lupus or nephrotoxic nephritis
- PMID: 20039408
- PMCID: PMC3625741
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27232
Lack of effect of a single injection of human C-reactive protein on murine lupus or nephrotoxic nephritis
Abstract
Objective: It has been reported that a single dose of human C-reactive protein (CRP) can prevent and reverse the renal damage in murine models of spontaneous lupus, as well as the rapid-onset immune complex disease induced in the accelerated nephrotoxic nephritis (ANTN) model. This study was undertaken to attempt to replicate these observations using a highly purified and fully characterized human CRP preparation.
Methods: (NZB x NZW)F(1) (NZB/NZW) mice were treated with a single 200-microg subcutaneous injection of CRP or control reagents either before disease onset at 4 months of age or when high-grade proteinuria was present at 7 months of age. Mice were monitored at least monthly for proteinuria and autoantibody levels. ANTN was induced by preimmunizing C57BL/6 mice with sheep IgG, followed 5 days later by injection of sheep anti-mouse glomerular basement membrane antibody and CRP or control reagents. Renal disease was assessed by regular urinalysis and histologic evaluation.
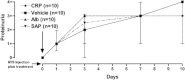
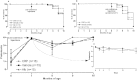
Results: CRP treatment of NZB/NZW mice, either early or late in the disease, had no effect on proteinuria, autoantibody titers, or survival. CRP administration did not reduce renal injury or alter disease in the ANTN model. Human serum amyloid P component, a pentraxin protein that is very closely related to CRP, similarly had no effect.
Conclusion: Our completely negative observations do not confirm that human CRP has reproducible antiinflammatory or immunomodulatory effects in these murine models, nor do they support the suggestion that CRP might be useful for therapy of lupus or immune complex-mediated nephritis.
Figures
References
-
- Du Clos TW. C-reactive protein reacts with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Immunol. 1989;143:2553–9. - PubMed
-
- Pepys MB. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet. 1981;1:653–7. - PubMed
-
- Pepys MB, Lanham JG, de Beer FC. C-reactive protein in systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Hughes GR, editor. Clinics in the rheumatic diseases. 1st ed. Eastbourne (UK): WB Saunders; 1982. pp. 91–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

