EspM2 is a RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- PMID: 20039879
- PMCID: PMC2871174
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01423.x
EspM2 is a RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Abstract
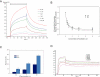
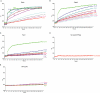
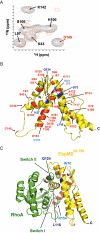
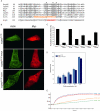
We investigated how the type III secretion system WxxxE effectors EspM2 of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli, which triggers stress fibre formation, and SifA of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, which is involved in intracellular survival, modulate Rho GTPases. We identified a direct interaction between EspM2 or SifA and nucleotide-free RhoA. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy revealed that EspM2 has a similar fold to SifA and the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) effector SopE. EspM2 induced nucleotide exchange in RhoA but not in Rac1 or H-Ras, while SifA induced nucleotide exchange in none of them. Mutating W70 of the WxxxE motif or L118 and I127 residues, which surround the catalytic loop, affected the stability of EspM2. Substitution of Q124, located within the catalytic loop of EspM2, with alanine, greatly attenuated the RhoA GEF activity in vitro and the ability of EspM2 to induce stress fibres upon ectopic expression. These results suggest that binding of SifA to RhoA does not trigger nucleotide exchange while EspM2 is a unique Rho GTPase GEF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EspO1-2 regulates EspM2-mediated RhoA activity to stabilize formation of focal adhesions in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-infected host cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055960. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409096 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial guanine nucleotide exchange factors SopE-like and WxxxE effectors.Infect Immun. 2010 Apr;78(4):1417-25. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01250-09. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20123714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of Salmonella SifA indicate that its interactions with SKIP, SseJ, and RhoA family GTPases induce endosomal tubulation.Cell Host Microbe. 2008 Nov 13;4(5):434-46. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.08.012. Cell Host Microbe. 2008. PMID: 18996344 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based functional analysis of effector protein SifA in living cells reveals motifs important for Salmonella intracellular proliferation.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jan;308(1):84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28939436
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of enteric pathogens by the nodosome.Trends Immunol. 2014 Mar;35(3):123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Trends Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24268520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EspO1-2 regulates EspM2-mediated RhoA activity to stabilize formation of focal adhesions in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-infected host cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055960. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409096 Free PMC article.
-
BID-F1 and BID-F2 domains of Bartonella henselae effector protein BepF trigger together with BepC the formation of invasome structures.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25106. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025106. Epub 2011 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22043280 Free PMC article.
-
The current Salmonella-host interactome.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012 Jan;6(1-2):117-33. doi: 10.1002/prca.201100083. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012. PMID: 22213674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial factors exploit eukaryotic Rho GTPase signaling cascades to promote invasion and proliferation within their host.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e28209. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.28209. Epub 2014 May 8. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25203748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alto NM, Shao F, Lazar CS, Brost RL, Chua G, Mattoo S, et al. Identification of a bacterial type III effector family with G protein mimicry functions. Cell. 2006;124:133–145. - PubMed
-
- Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:195–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

