The effect of DPP-4 inhibition with sitagliptin on incretin secretion and on fasting and postprandial glucose turnover in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- PMID: 20039889
- PMCID: PMC2908732
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03764.x
The effect of DPP-4 inhibition with sitagliptin on incretin secretion and on fasting and postprandial glucose turnover in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
Abstract
Objective: Low glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) concentrations have been observed in impaired fasting glucose (IFG). It is uncertain whether these abnormalities contribute directly to the pathogenesis of IFG and impaired glucose tolerance. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors raise incretin hormone concentrations enabling an examination of their effects on glucose turnover in IFG.
Research design and methods: We studied 22 subjects with IFG using a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel-group design. At the time of enrollment, subjects ate a standardized meal labelled with [1-(13)C]-glucose. Infused [6-(3)H] glucose enabled measurement of systemic meal appearance (MRa). Infused [6,6-(2)H(2)] glucose enabled measurement of endogenous glucose production (EGP) and glucose disappearance (Rd). Subsequently, subjects were randomized to 100 mg of sitagliptin daily or placebo. After an 8-week treatment period, the mixed meal was repeated.
Results: As expected, subjects with IFG who received placebo did not experience any change in glucose concentrations. Despite raising intact GLP-1 concentrations, treatment with sitagliptin did not alter either fasting or postprandial glucose, insulin or C-peptide concentrations. Postprandial EGP (18.1 +/- 0.7 vs 17.6 +/- 0.8 micromol/kg per min, P = 0.53), Rd (55.6 +/- 4.3 vs 58.9 +/- 3.3 micromol/kg per min, P = 0.47) and MRa (6639 +/- 377 vs 6581 +/- 316 micromol/kg per 6 h, P = 0.85) were unchanged. Sitagliptin was associated with decreased total GLP-1 implying decreased incretin secretion.
Conclusions: DPP-4 inhibition did not alter fasting or postprandial glucose turnover in people with IFG. Low incretin concentrations are unlikely to be involved in the pathogenesis of IFG.
Figures
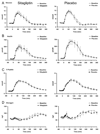
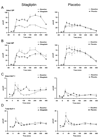
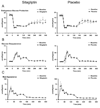
References
-
- Tirosh A, Shai I, Tekes-Manova D, Israeli E, Pereg D, Shochat T, et al. Normal fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes in young men. N Engl J Med. 2005 Oct 6;353(14):1454–1462. - PubMed
-
- Bock G, Dalla Man C, Campioni M, Chittilapilly E, Basu R, Toffolo G, et al. Pathogenesis of pre-diabetes: mechanisms of fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in people with impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 2006 Dec;55(12):3536–3549. - PubMed
-
- Rask E, Olsson T, Soderberg S, Holst Jj J, Tura A, Pacini G, et al. Insulin secretion and incretin hormones after oral glucose in non-obese subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Metabolism. 2004 May;53(5):624–631. - PubMed
-
- Toft-Nielsen MB, Damholt MB, Madsbad S, Hilsted LM, Hughes TE, Michelsen BK, et al. Determinants of the impaired secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Aug;86(8):3717–3723. - PubMed
-
- Laakso M, Zilinskaite J, Hansen T, Boesgaard TW, Vanttinen M, Stancakova A, et al. Insulin sensitivity, insulin release and glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in persons with impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance in the EUGENE2 study. Diabetologia. 2008 Mar;51(3):502–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

